Will A GenAI Like ChatGPT Replace Google Search?
In this article, we will explore how GenAI and traditional search engines work, compare their strengths and weaknesses, and discuss the potential for integrating both technologies.
Read the entire series
- What is Information Retrieval?
- Information Retrieval Metrics
- Search Still Matters: Enhancing Information Retrieval with Generative AI and Vector Databases
- Hybrid Search: Combining Text and Image for Enhanced Search Capabilities
- What Are Rerankers and How Do They Enhance Information Retrieval?
- Understanding Boolean Retrieval Models in Information Retrieval
- Will A GenAI Like ChatGPT Replace Google Search?
- The Evolution of Search: From Traditional Keyword Matching to Vector Search and Generative AI
- What is a Knowledge Graph (KG)?
Search engines have been our go-to tools for finding information online for decades. From simple queries to complex research, we rely on engines like Google to find the information we’re looking for out of billions of web pages, delivering the most relevant results in seconds. However, recent advancements in artificial intelligence are beginning to challenge this traditional approach.
Generative AI (GenAI), particularly large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, has made a significant step towards replacing Search Engines. These AI tools are pre-trained on massive amounts of data and can understand and generate human-like text that offers detailed and context-aware responses in almost every area. This raises an important question: could generative AI replace traditional search engines?
In this article, we will explore how GenAI and traditional search engines work, compare their strengths and weaknesses, and discuss the potential for integrating both technologies.
Understanding Generative AI and Its Capabilities
Generative AI or GenAI refers to a class of artificial intelligence models that can generate new content, from text and images to music and more. Unlike traditional AI technologies, which focus on recognizing patterns and making predictions, generative AI creates original content based on the input it has been given (prompt) and the data it has been trained on. These models use complex algorithms to understand and mimic human language, making them incredibly versatile and powerful.
The development of GenAI has seen rapid progress over the past few decades. Early AI models were rule-based systems with limited capabilities. However, the rise of machine learning and neural networks in the 2000s marked a significant leap forward. Researchers began developing models that could learn from large datasets and improve their performance over time.
A major breakthrough came with Google researchers' introduction of the Transformer architecture in 2017. This architecture enabled the creation of large-scale language models that could process and generate text with unprecedented accuracy. Building on this foundation, OpenAI developed the Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) series, with GPT-4 being the most advanced iteration to date.
ChatGPT and the AI Models Behind It
ChatGPT, developed by OpenAI, is based on the GPT-3 and GPT-4 models. GPT stands for Generative Pre-trained Transformer and is one of the largest and most powerful large language models (LLMs) ever created. It has 175 billion parameters, which are the weights and biases the model adjusts during training to improve its accuracy.
GPT-3 was trained on a diverse range of internet text, enabling it to generate coherent and contextually relevant responses to various prompts. When you ask ChatGPT a question or give it a task, it analyzes the input, predicts the most likely next words, and generates a response that follows the context and style of human conversation.
ChatGPT's capabilities are vast. It can answer questions, write essays, generate creative content, provide tutoring in various subjects, and even engage in complex conversations. Its ability to understand context and generate human-like text makes it a powerful tool for many applications.
However, it's important to note that while ChatGPT is highly advanced, it also has limitations. It can sometimes produce incorrect or nonsensical answers, which are known as hallucinations, and it may struggle with understanding nuanced or ambiguous queries. A technique called retrieval augmented generation (RAG) emerges to mitigate these hallucinations. It usually comprises a vector database like Milvus, an embedding model, and an LLM. The vector database provides contextual information to the LLM so that the model can generate more accurate and relevant answers to user queries.
Despite these challenges, the progress in generative AI represented by models like ChatGPT is remarkable and continues to push the boundaries of what AI can achieve.
Traditional Search Engines and How They Work
Traditional search engines, like Google, are tools designed to help users find information online. They crawl, index, and rank web pages to deliver the most relevant results to users' queries.
A search engine is a software system that searches for information on the internet based on a user's query. When you enter a search term, the search engine scans its index of web pages and returns a list of results that best match your query. These results can include web pages, images, videos, news articles, and other types of content.
Key Search Components: Crawling, Indexing, and Ranking
Crawling: Search engines use automated programs called crawlers or spiders to browse the web and discover new or updated content. These crawlers follow links from one page to another, gathering data about each page they visit.
Indexing: Once a page is crawled, the search engine processes the information and adds it to its index. The index is a massive database of all the content the search engine has discovered and marked relevant. This database allows the search engine to quickly retrieve and display relevant results when a user searches.
Ranking: When a user enters a query, the search engine uses complex algorithms to rank the indexed pages based on their relevance to the query. The goal is to present the most useful and relevant results at the top of the search results page.
Ranking Algorithms of Traditional Search
One of the most well-known ranking algorithms is Google's PageRank. PageRank evaluates the importance of web pages based on the number and quality of links pointing to them (known as backlinks). The basic idea is that pages with high-quality inbound links are more authoritative and relevant.
Several factors influence how search engines rank pages. Although the ranking algorithms change with time, some of the common factors include:
Relevance: How well the content of a page matches the user's query. This includes the presence of the relevant keywords related to the topic, the context of the content, and how well it addresses the search intent.
Authority: The credibility and trustworthiness of a page, often determined by the quality and quantity of inbound links from other reputable sites.
User Behavior: Search engines also consider how users interact with search results. Metrics like click-through rate (CTR), time spent on a page, and bounce rate can indicate a page's relevance and quality.
ChatGPT vs. Traditional Search Engines: A Comprehensive Comparison
Let’s compare ChatGPT and traditional search engines in the following key aspects.
Answer Generation and Information Retrieval
ChatGPT understands user intent and generates direct, conversational responses. It interprets complex queries and delivers contextually relevant answers in a human-like manner. For instance, if asked to explain a technical concept like HNSW, ChatGPT can provide a detailed and simplified explanation, adapting its response to the ongoing conversation. This makes it particularly useful for interactive, dialogue-based information retrieval, where users seek quick, personalized answers.
Traditional search engines like Google operate differently. Instead of generating answers, they retrieve and rank links to web pages that contain the relevant information. These search engines crawl the web, index vast amounts of content, and use sophisticated algorithms to rank results based on relevance, authority, and user behavior. This method allows users to access a broad spectrum of content, from scholarly articles and news reports to videos and blog posts, offering a comprehensive overview of available information.
Authority, Trustworthiness, and Reliability
While ChatGPT is powerful in generating content, it faces challenges in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of its responses. This model and many other LLMs generate text based on patterns learned from its training data, which can sometimes lead to incorrect or misleading information, known as "hallucinations." Additionally, ChatGPT does not have access to real-time information, meaning its answers can be outdated. The lack of direct links to verified sources also limits users' ability to cross-check the information provided.
Search engines like Google prioritize authority and trustworthiness in their search results. They rank content based on factors such as relevance, the authority of the source, and the quality of inbound links. Algorithms like PageRank evaluate the trustworthiness of web pages, ensuring that the top search results come from reliable sources. This method allows users to verify information across multiple authoritative sources, providing a higher confidence in the content they access. However, the drawback is they can overwhelm users with abundant results, making it difficult to find the most relevant information quickly.
Real-Time Information and Updates
One significant limitation of ChatGPT is its inability to provide real-time information. Its knowledge is based on a static dataset with a cutoff date, so it cannot offer updates on current events, recent scientific discoveries, or any developments beyond its last training period. This limits its usefulness for queries requiring the most up-to-date information.
In contrast, traditional search engines continuously index new content and provide real-time information. Users can quickly access the latest news, research, and developments, making these platforms more suitable for queries that demand current and continuously updated information.
Understanding and Handling Complex Queries
ChatGPT’s strength lies in its ability to understand and respond to nuanced, context-rich queries. It can engage in multi-turn conversations, where it builds on previous exchanges to provide more refined answers. This ability makes it ideal for users seeking detailed explanations or those who need to ask follow-up questions to clarify their understanding.
While traditional search engines effectively retrieve information based on keywords, they struggle with complex or nuanced queries that require contextual understanding. Users may need to refine their search terms or sift through multiple pages to find the desired information, especially if the initial query is ambiguous or not well-phrased.
Ethical Concerns and Bias in AI Content
LLMs like ChatGPT can reflect and amplify biases in their training data, raising ethical concerns. This can lead to the generation of biased or even harmful content, often unintentionally. Additionally, risks are associated with using AI-generated content for malicious purposes, such as spreading misinformation or creating deceptive materials. These ethical challenges necessitate careful consideration and ongoing efforts to ensure the responsible development and use of AI.
Traditional search engines are not free from bias, but they present a wide range of information from various sources, allowing users to compare and contrast different perspectives. However, search engines rely heavily on ranking algorithms to determine the order of search results. These algorithms can be manipulated through SEO (Search Engine Optimization) practices, which aim to increase the visibility of web pages.
The table below summarizes the key differences between ChatGPT and traditional search engines.
| Aspect | ChatGPT | Traditional Search Engines |
| Understanding User Intent | Excellent at understanding and providing direct, conversational answers | Good at matching keywords but may struggle with nuanced queries |
| Information Retrieval | Generates text based on training data, not real-time information | Crawls, indexes, and retrieves vast amounts of web data in real-time |
| Response Generation | Provides detailed, human-like responses | Provides links to relevant sources, requiring user navigation |
| Accuracy | Can produce incorrect or misleading information (hallucinations) | Uses algorithms to rank authoritative sources, generally reliable |
| Real-Time Updates | Limited to data up to its training cutoff date | Continuously updates with new content from the web |
| Ethical Concerns | Prone to biases in training data, ethical use concerns | Issues with SEO manipulation and ranking fairness |
| User Experience | Interactive and conversational, ideal for specific questions | Efficient for broad searches and accessing a wide range of content |
| Data Sources | Trained on diverse internet text up to a certain date | Continuously crawls and indexes current web content |
| Reliability | Can struggle with providing consistent, accurate information | Generally reliable, especially for well-established topics |
| Use Cases | Ideal for personalized tutoring, creative writing, and conversational tasks | Best for comprehensive research, finding specific documents, and broad information searches |
Table: Comparing ChatGPT and Traditional Search
Will ChatGPT Replace Search Engines?
The question of whether ChatGPT will replace traditional search engines is intriguing but complex. While ChatGPT brings innovative features like generating conversational and contextually relevant responses, it also has limitations, such as the potential for hallucinations, outdated information, and response bias. Similarly, traditional search engines offer significant benefits and have powered countless users and applications, yet they struggle with generating human-like answers and handling complex multi-hop questions.
Given these factors, it's unlikely that ChatGPT will fully replace traditional search engines in the foreseeable future. Instead, the future of search will likely evolve to integrate generative AI with traditional search engines. By combining the strengths of both technologies, we can create a more efficient search experience—where generative AI delivers direct, conversational answers and traditional search engines provide a comprehensive list of sources to ensure accuracy and authority.
Real-World Examples of the Hybrid AI and Search Approach
Companies like Google and Microsoft are integrating AI into their search engines. Google uses AI to provide featured snippets and quick answers at the top of search results. Microsoft's Bing also incorporates AI to provide intelligent answers and summarize search results. These efforts show the benefits of combining AI with traditional search technology.
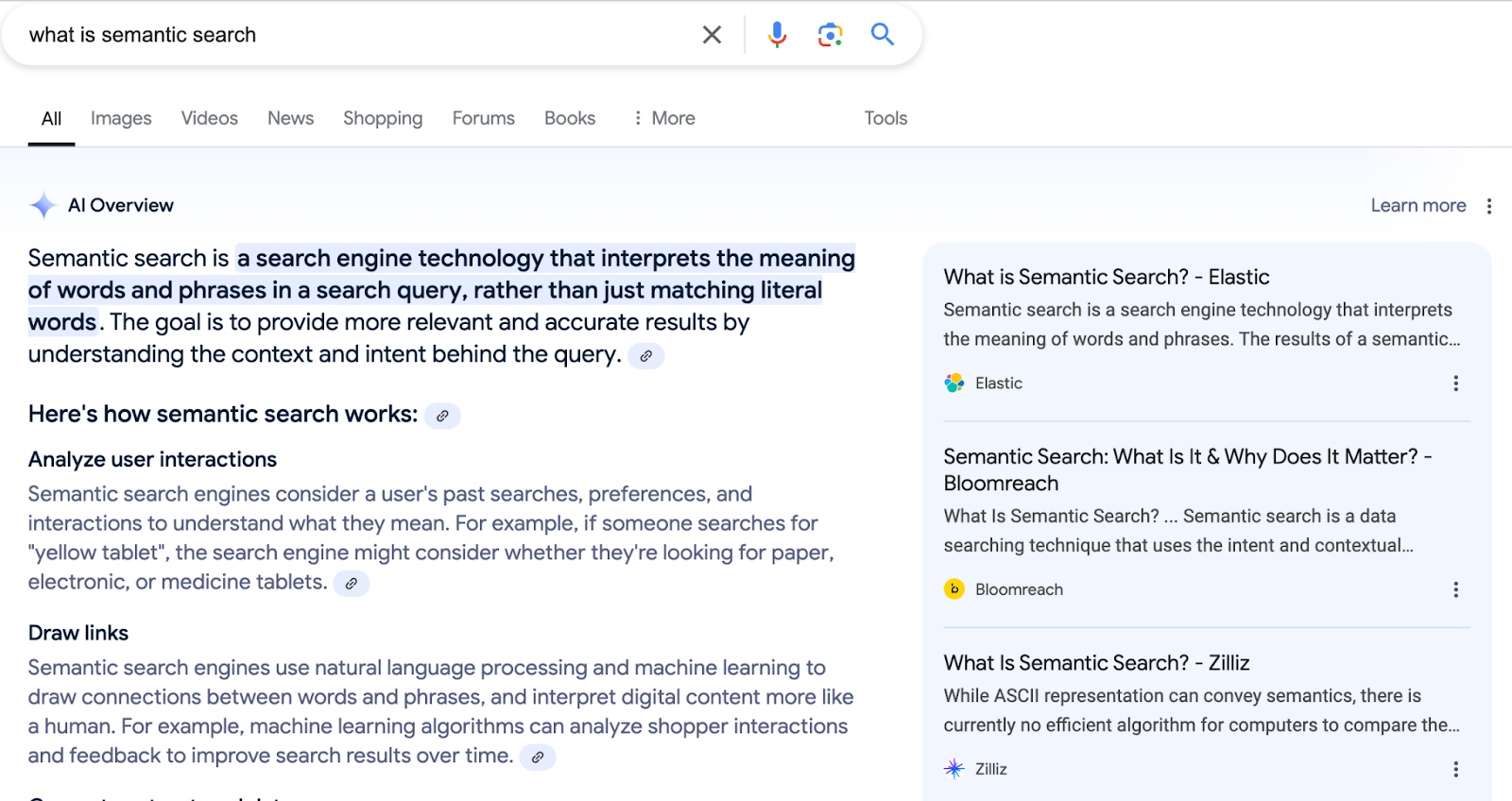 Figure- An example of Google’s Hybrid AI and Search Approach
Figure- An example of Google’s Hybrid AI and Search Approach
Google has also been testing generative AI tools to enhance search functionality. These tools aim to provide more detailed and contextually relevant answers but have sparked controversy over accuracy and bias. Despite these challenges, AI's potential to transform search remains significant.
The Role of Vector Databases in Hybrid AI and Search
A vector database is a data management system that stores, indexes, and searches unstructured data through numerical representations called vector embeddings in a high-dimensional space for fast semantic information retrieval and vector similarity search. Milvus and Zilliz Cloud (fully managed Milvus) are two primary examples of purpose-built vector databases that can handle billion-scale vector data.
By integrating Milvus with LLMs, companies can implement robust Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. These systems can mitigate the hallucination issues in LLMs by combining search engines' real-time data retrieval strengths with the context-aware generative capabilities of AI models like ChatGPT. This synergy can also significantly improve search technologies' accuracy, relevance, and user experience, paving the way for the next generation of information retrieval systems.
Check out this video to learn more about Milvus and vector databases.
Conclusion
Generative AI, like ChatGPT, has redefined how we interact with information by providing direct, conversational responses. However, it faces challenges such as accuracy, real-time updates, and ethical concerns. Traditional search engines excel at indexing vast amounts of information and ensuring its relevance and authority but can be overwhelmed by too many results and struggle with nuanced queries.
The future of search likely lies in a hybrid AI and search approach, combining the strengths of Generative AI and traditional search engines. This integration promises a more efficient and intuitive search experience, offering both direct answers and comprehensive resources. As innovations continue, AI and traditional search engines will likely coexist and complement each other, enhancing how we access and interact with information online.
Further Resources
- Understanding Generative AI and Its Capabilities
- Traditional Search Engines and How They Work
- ChatGPT vs. Traditional Search Engines: A Comprehensive Comparison
- Will ChatGPT Replace Search Engines?
- The Role of Vector Databases in Hybrid AI and Search
- Conclusion
- Further Resources
Content
Start Free, Scale Easily
Try the fully-managed vector database built for your GenAI applications.
Try Zilliz Cloud for FreeKeep Reading

What is Information Retrieval?
Information retrieval (IR) is the process of efficiently retrieving relevant information from large collections of unstructured or semi-structured data.

Search Still Matters: Enhancing Information Retrieval with Generative AI and Vector Databases
Despite advances in LLMs like ChatGPT, search still matters. Combining GenAI with search and vector databases enhances search accuracy and experience.

Hybrid Search: Combining Text and Image for Enhanced Search Capabilities
Milvus enables hybrid sparse and dense vector search and multi-vector search capabilities, simplifying the vectorization and search process.
