Build RAG Chatbot with LangChain, Zilliz Cloud, Cohere Command R, and Ollama nomic-embed-text
Introduction to RAG
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a game-changer for GenAI applications, especially in conversational AI. It combines the power of pre-trained large language models (LLMs) like OpenAI’s GPT with external knowledge sources stored in vector databases such as Milvus and Zilliz Cloud, allowing for more accurate, contextually relevant, and up-to-date response generation. A RAG pipeline usually consists of four basic components: a vector database, an embedding model, an LLM, and a framework.
Key Components We'll Use for This RAG Chatbot
This tutorial shows you how to build a simple RAG chatbot in Python using the following components:
- LangChain: An open-source framework that helps you orchestrate the interaction between LLMs, vector stores, embedding models, etc, making it easier to integrate a RAG pipeline.
- Zilliz Cloud: a fully managed vector database-as-a-service platform built on top of the open-source Milvus, designed to handle high-performance vector data processing at scale. It enables organizations to efficiently store, search, and analyze large volumes of unstructured data, such as text, images, or audio, by leveraging advanced vector search technology. It offers a free tier supporting up to 1 million vectors.
- Cohere Command R: This model is designed for high-performance retrieval tasks, offering advanced capabilities in understanding and generating natural language. Its strengths lie in semantic search and document summarization, making it ideal for applications such as customer support, content generation, and knowledge management, where accuracy and context relevance are paramount.
- Ollama nomic-embed-text: This model specializes in generating high-quality text embeddings, designed to enhance semantic understanding in various NLP tasks. Its strengths lie in contextual representation and scalability, making it suitable for applications like semantic search, recommendation systems, and clustering. Ideal for developers looking to integrate profound text analysis into their projects.
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have a functional chatbot capable of answering questions based on a custom knowledge base.
Note: Since we may use proprietary models in our tutorials, make sure you have the required API key beforehand.
Step 1: Install and Set Up LangChain
%pip install --quiet --upgrade langchain-text-splitters langchain-community langgraph
Step 2: Install and Set Up Cohere Command R
pip install -qU "langchain[cohere]"
import getpass
import os
if not os.environ.get("COHERE_API_KEY"):
os.environ["COHERE_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass("Enter API key for Cohere: ")
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
llm = init_chat_model("command-r", model_provider="cohere")
Step 3: Install and Set Up Ollama nomic-embed-text
pip install -qU langchain-ollama
from langchain_ollama import OllamaEmbeddings
embeddings = OllamaEmbeddings(model="nomic-embed-text")
Step 4: Install and Set Up Zilliz Cloud
pip install -qU langchain-milvus
from langchain_milvus import Zilliz
vector_store = Zilliz(
embedding_function=embeddings,
connection_args={
"uri": ZILLIZ_CLOUD_URI,
"token": ZILLIZ_CLOUD_TOKEN,
},
)
Step 5: Build a RAG Chatbot
Now that you’ve set up all components, let’s start to build a simple chatbot. We’ll use the Milvus introduction doc as a private knowledge base. You can replace it with your own dataset to customize your RAG chatbot.
import bs4
from langchain import hub
from langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoader
from langchain_core.documents import Document
from langchain_text_splitters import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
from langgraph.graph import START, StateGraph
from typing_extensions import List, TypedDict
# Load and chunk contents of the blog
loader = WebBaseLoader(
web_paths=("https://milvus.io/docs/overview.md",),
bs_kwargs=dict(
parse_only=bs4.SoupStrainer(
class_=("doc-style doc-post-content")
)
),
)
docs = loader.load()
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=1000, chunk_overlap=200)
all_splits = text_splitter.split_documents(docs)
# Index chunks
_ = vector_store.add_documents(documents=all_splits)
# Define prompt for question-answering
prompt = hub.pull("rlm/rag-prompt")
# Define state for application
class State(TypedDict):
question: str
context: List[Document]
answer: str
# Define application steps
def retrieve(state: State):
retrieved_docs = vector_store.similarity_search(state["question"])
return {"context": retrieved_docs}
def generate(state: State):
docs_content = "\n\n".join(doc.page_content for doc in state["context"])
messages = prompt.invoke({"question": state["question"], "context": docs_content})
response = llm.invoke(messages)
return {"answer": response.content}
# Compile application and test
graph_builder = StateGraph(State).add_sequence([retrieve, generate])
graph_builder.add_edge(START, "retrieve")
graph = graph_builder.compile()
Test the Chatbot
Yeah! You've built your own chatbot. Let's ask the chatbot a question.
response = graph.invoke({"question": "What data types does Milvus support?"})
print(response["answer"])
Example Output
Milvus supports various data types including sparse vectors, binary vectors, JSON, and arrays. Additionally, it handles common numerical and character types, making it versatile for different data modeling needs. This allows users to manage unstructured or multi-modal data efficiently.
Optimization Tips
As you build your RAG system, optimization is key to ensuring peak performance and efficiency. While setting up the components is an essential first step, fine-tuning each one will help you create a solution that works even better and scales seamlessly. In this section, we’ll share some practical tips for optimizing all these components, giving you the edge to build smarter, faster, and more responsive RAG applications.
LangChain optimization tips
To optimize LangChain, focus on minimizing redundant operations in your workflow by structuring your chains and agents efficiently. Use caching to avoid repeated computations, speeding up your system, and experiment with modular design to ensure that components like models or databases can be easily swapped out. This will provide both flexibility and efficiency, allowing you to quickly scale your system without unnecessary delays or complications.
Zilliz Cloud optimization tips
Optimizing Zilliz Cloud for a RAG system involves efficient index selection, query tuning, and resource management. Use Hierarchical Navigable Small World (HNSW) indexing for high-speed, approximate nearest neighbor search while balancing recall and efficiency. Fine-tune ef_construction and M parameters based on your dataset size and query workload to optimize search accuracy and latency. Enable dynamic scaling to handle fluctuating workloads efficiently, ensuring smooth performance under varying query loads. Implement data partitioning to improve retrieval speed by grouping related data, reducing unnecessary comparisons. Regularly update and optimize embeddings to keep results relevant, particularly when dealing with evolving datasets. Use hybrid search techniques, such as combining vector and keyword search, to improve response quality. Monitor system metrics in Zilliz Cloud’s dashboard and adjust configurations accordingly to maintain low-latency, high-throughput performance.
Cohere Command R optimization tips
Cohere Command R is designed for retrieval-augmented generation, making efficient context retrieval and ranking critical for system performance. Optimize retrieval pipelines by using Cohere’s embedding-based search to identify and rank the most relevant documents, reducing unnecessary input context while maintaining accuracy. Improve response quality by fine-tuning temperature settings; lower values (0.1–0.2) work best for structured, fact-based queries, while higher values introduce more variability in generated responses. Utilize prompt templates to maintain consistent formatting, ensuring clarity in output. Implement batch processing where multiple queries need similar context, reducing redundant API calls. To enhance efficiency, cache top query results and leverage incremental context updates instead of repeatedly sending full document sets. If deploying at scale, monitor latency and response consistency with real-time metrics, adjusting retrieval thresholds dynamically for optimal balance between speed and completeness.
Ollama nomic-embed-text optimization tips
Ollama nomic-embed-text is designed for robust text embedding generation, making it essential to optimize how embeddings are stored and queried in a RAG pipeline. Preprocess input text by stripping unnecessary metadata and normalizing case to maintain consistency. Choose an optimized vector indexing strategy, such as IVF-PQ for balanced speed and accuracy, depending on dataset size. Use approximate nearest neighbor search to accelerate retrieval while maintaining a high recall rate. Cache commonly accessed embeddings to avoid redundant computations. If embeddings are used for long-term retrieval tasks, periodically refresh and retrain on new data to prevent model drift. Optimize database queries to quickly retrieve relevant embeddings and minimize I/O bottlenecks.
By implementing these tips across your components, you'll be able to enhance the performance and functionality of your RAG system, ensuring it’s optimized for both speed and accuracy. Keep testing, iterating, and refining your setup to stay ahead in the ever-evolving world of AI development.
RAG Cost Calculator: A Free Tool to Calculate Your Cost in Seconds
Estimating the cost of a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline involves analyzing expenses across vector storage, compute resources, and API usage. Key cost drivers include vector database queries, embedding generation, and LLM inference.
RAG Cost Calculator is a free tool that quickly estimates the cost of building a RAG pipeline, including chunking, embedding, vector storage/search, and LLM generation. It also helps you identify cost-saving opportunities and achieve up to 10x cost reduction on vector databases with the serverless option.
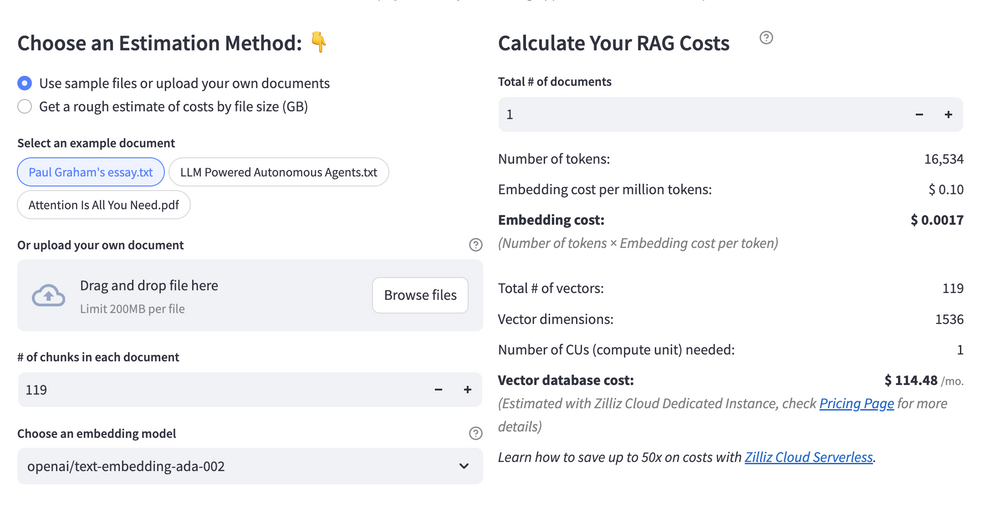 Calculate your RAG cost
Calculate your RAG cost
What Have You Learned?
What a journey we’ve been on together! Over the course of this tutorial, you’ve witnessed how the integration of a powerful framework, a cutting-edge vector database, a sophisticated LLM, and a robust embedding model can come together to create an impressive retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) system. Think about it: the framework provided the backbone, seamlessly tying all these components together, allowing for a workflow that’s both efficient and intuitive. The vector database unleashed lightning-fast search capabilities, enabling you to access expansive datasets with remarkable speed and accuracy. The LLM? It’s like having your own conversational wizard, transforming data into coherent, insightful dialogues. And let’s not forget the embedding model that enriched our semantic understanding, ensuring that the responses were not just accurate but deeply relevant to user queries.
Along the way, we’ve sprinkled in some optimization tips and provided you with a handy cost calculator to ensure you’re not just dreaming big but also planning smartly. Now that you’re equipped with this knowledge, the possibilities are endless! Dive in, start building, and let your creativity shine. Innovate your own RAG applications and push the boundaries of what’s possible. Remember, every great creation starts with a single step—so why wait? Get out there and make it happen!
Further Resources
🌟 In addition to this RAG tutorial, unleash your full potential with these incredible resources to level up your RAG skills.
- How to Build a Multimodal RAG | Documentation
- How to Enhance the Performance of Your RAG Pipeline
- Graph RAG with Milvus | Documentation
- How to Evaluate RAG Applications - Zilliz Learn
- Generative AI Resource Hub | Zilliz
We'd Love to Hear What You Think!
We’d love to hear your thoughts! 🌟 Leave your questions or comments below or join our vibrant Milvus Discord community to share your experiences, ask questions, or connect with thousands of AI enthusiasts. Your journey matters to us!
If you like this tutorial, show your support by giving our Milvus GitHub repo a star ⭐—it means the world to us and inspires us to keep creating! 💖
- Introduction to RAG
- Key Components We'll Use for This RAG Chatbot
- Step 1: Install and Set Up LangChain
- Step 2: Install and Set Up Cohere Command R
- Step 3: Install and Set Up Ollama nomic-embed-text
- Step 4: Install and Set Up Zilliz Cloud
- Step 5: Build a RAG Chatbot
- Optimization Tips
- RAG Cost Calculator: A Free Tool to Calculate Your Cost in Seconds
- What Have You Learned?
- Further Resources
- We'd Love to Hear What You Think!
Content
Vector Database at Scale
Zilliz Cloud is a fully-managed vector database built for scale, perfect for your RAG apps.
Try Zilliz Cloud for Free


