Build RAG Chatbot with Llamaindex, Pgvector, OpenAI GPT-o1, and Mistral Embed
Introduction to RAG
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a game-changer for GenAI applications, especially in conversational AI. It combines the power of pre-trained large language models (LLMs) like OpenAI’s GPT with external knowledge sources stored in vector databases such as Milvus and Zilliz Cloud, allowing for more accurate, contextually relevant, and up-to-date response generation. A RAG pipeline usually consists of four basic components: a vector database, an embedding model, an LLM, and a framework.
Key Components We'll Use for This RAG Chatbot
This tutorial shows you how to build a simple RAG chatbot in Python using the following components:
- Llamaindex: a data framework that connects large language models (LLMs) with various data sources, enabling efficient retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). It helps structure, index, and query private or external data, optimizing LLM applications for search, chatbots, and analytics.
- Pgvector: an open-source extension for PostgreSQL that enables efficient storage and querying of high-dimensional vector data, essential for machine learning and AI applications. Designed to handle embeddings, it supports fast approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) searches using algorithms like HNSW and IVFFlat. Since it is just a vector search add-on to traditional search rather than a purpose-built vector database, it lacks scalability and availability and many other advanced features required by enterprise-level applications. Therefore, if you prefer a much more scalable solution or hate to manage your own infrastructure, we recommend using Zilliz Cloud, which is a fully managed vector database service built on the open-source Milvus and offers a free tier supporting up to 1 million vectors.)
- OpenAI GPT-1: A foundational transformer-based language model designed for natural language understanding and generation. Strengths include coherent text generation, contextual comprehension, and adaptability to diverse NLP tasks. Ideal for text completion, basic conversational agents, and early-stage language research, serving as a precursor to more advanced models like GPT-3 and GPT-4.
- Mistral Embed: A high-performance embedding model designed to convert text into dense vector representations, capturing semantic meaning for tasks like retrieval, clustering, and similarity analysis. It excels in efficiency, multilingual support, and scalability, making it ideal for semantic search engines, multilingual content organization, and large-scale data processing applications requiring rapid, context-aware text analysis.
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have a functional chatbot capable of answering questions based on a custom knowledge base.
Note: Since we may use proprietary models in our tutorials, make sure you have the required API key beforehand.
Step 1: Install and Set Up Llamaindex
pip install llama-index
Step 2: Install and Set Up OpenAI GPT-o1
%pip install llama-index llama-index-llms-openai
from llama_index.llms.openai import OpenAI
llm = OpenAI(
model="o1",
# api_key="some key", # uses OPENAI_API_KEY env var by default
)
Step 3: Install and Set Up Mistral Embed
%pip install llama-index-embeddings-mistralai
# imports
from llama_index.embeddings.mistralai import MistralAIEmbedding
# get API key and create embeddings
api_key = "YOUR API KEY"
model_name = "mistral-embed"
embed_model = MistralAIEmbedding(model_name=model_name, api_key=api_key)
Step 4: Install and Set Up Pgvector
%pip install llama-index-vector-stores-postgres
from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex
from llama_index.vector_stores.postgres import PGVectorStore
vector_store = PGVectorStore.from_params(
database=db_name,
host=url.host,
password=url.password,
port=url.port,
user=url.username,
table_name="your_table_name",
embed_dim=1536, # openai embedding dimension
hnsw_kwargs={
"hnsw_m": 16,
"hnsw_ef_construction": 64,
"hnsw_ef_search": 40,
"hnsw_dist_method": "vector_cosine_ops",
},
)
Step 5: Build a RAG Chatbot
Now that you’ve set up all components, let’s start to build a simple chatbot. We’ll use the Milvus introduction doc as a private knowledge base. You can replace it with your own dataset to customize your RAG chatbot.
import requests
from llama_index.core import SimpleDirectoryReader
# load documents
url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/milvus-io/milvus-docs/refs/heads/v2.5.x/site/en/about/overview.md'
example_file = 'example_file.md' # You can replace it with your own file paths.
response = requests.get(url)
with open(example_file, 'wb') as f:
f.write(response.content)
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader(
input_files=[example_file]
).load_data()
print("Document ID:", documents[0].doc_id)
storage_context = StorageContext.from_defaults(vector_store=vector_store)
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(
documents, storage_context=storage_context, embed_model=embed_model
)
query_engine = index.as_query_engine(llm=llm)
res = query_engine.query("What is Milvus?") # You can replace it with your own question.
print(res)
Example output
Milvus is a high-performance, highly scalable vector database designed to operate efficiently across various environments, from personal laptops to large-scale distributed systems. It is available as both open-source software and a cloud service. Milvus excels in managing unstructured data by converting it into numerical vectors through embeddings, which facilitates fast and scalable searches and analytics. The database supports a wide range of data types and offers robust data modeling capabilities, allowing users to organize their data effectively. Additionally, Milvus provides multiple deployment options, including a lightweight version for quick prototyping and a distributed version for handling massive data scales.
Optimization Tips
As you build your RAG system, optimization is key to ensuring peak performance and efficiency. While setting up the components is an essential first step, fine-tuning each one will help you create a solution that works even better and scales seamlessly. In this section, we’ll share some practical tips for optimizing all these components, giving you the edge to build smarter, faster, and more responsive RAG applications.
LlamaIndex optimization tips
To optimize LlamaIndex for a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) setup, structure your data efficiently using hierarchical indices like tree-based or keyword-table indices for faster retrieval. Use embeddings that align with your use case to improve search relevance. Fine-tune chunk sizes to balance context length and retrieval precision. Enable caching for frequently accessed queries to enhance performance. Optimize metadata filtering to reduce unnecessary search space and improve speed. If using vector databases, ensure indexing strategies align with your query patterns. Implement async processing to handle large-scale document ingestion efficiently. Regularly monitor query performance and adjust indexing parameters as needed for optimal results.
pgvector optimization tips
To optimize pgvector in a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) setup, consider indexing your vectors using GiST or IVFFlat to significantly speed up search queries and improve retrieval performance. Make sure to leverage parallelization for query execution, allowing multiple queries to be processed simultaneously, especially for large datasets. Optimize memory usage by tuning the vector storage size and using compressed embeddings where possible. To further enhance query speed, implement pre-filtering techniques to narrow down search space before querying. Regularly rebuild indexes to ensure they are up to date with any new data. Fine-tune vectorization models to reduce dimensionality without sacrificing accuracy, thus improving both storage efficiency and retrieval times. Finally, manage resource allocation carefully, utilizing horizontal scaling for larger datasets and offloading intensive operations to dedicated processing units to maintain responsiveness during high-traffic periods.
OpenAI GPT-01 optimization tips
To optimize OpenAI GPT-01 in a RAG setup, fine-tune prompts to include explicit instructions and structured context (e.g., “Answer using: [retrieved text]”). Limit response length with max_tokens to reduce verbosity and cost. Use a lower temperature (0.2–0.5) for factual accuracy. Preprocess retrieved documents to remove irrelevant content, ensuring inputs fit token limits. Cache frequent queries to minimize API calls. Experiment with chunking strategies for context injection and prioritize critical information at the prompt’s start or end. Monitor latency and adjust batch sizes for throughput efficiency.
Mistral Embed optimization tips
To optimize Mistral Embed in a RAG setup, preprocess text by removing redundant whitespace, special characters, and normalizing casing to reduce embedding noise. Use batch processing for bulk embeddings to leverage GPU parallelism. Fine-tune Mistral Embed on domain-specific data if retrieval accuracy is low. Reduce input sequence length via truncation or sliding windows for long documents. Cache frequent queries to save compute. Test different pooling strategies (mean, max) for sentence-level embeddings and normalize outputs to improve similarity scoring consistency.
By implementing these tips across your components, you'll be able to enhance the performance and functionality of your RAG system, ensuring it’s optimized for both speed and accuracy. Keep testing, iterating, and refining your setup to stay ahead in the ever-evolving world of AI development.
RAG Cost Calculator: A Free Tool to Calculate Your Cost in Seconds
Estimating the cost of a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline involves analyzing expenses across vector storage, compute resources, and API usage. Key cost drivers include vector database queries, embedding generation, and LLM inference.
RAG Cost Calculator is a free tool that quickly estimates the cost of building a RAG pipeline, including chunking, embedding, vector storage/search, and LLM generation. It also helps you identify cost-saving opportunities and achieve up to 10x cost reduction on vector databases with the serverless option.
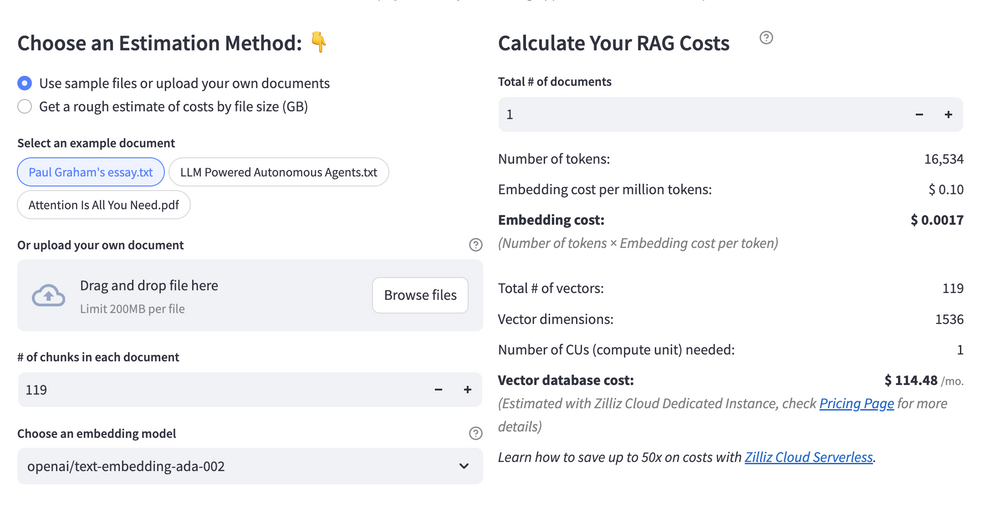 Calculate your RAG cost
Calculate your RAG cost
What Have You Learned?
Wow, what a journey we've embarked on together in this tutorial! You’ve learned how to weave together four powerful components into a robust Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system—LlamaIndex, Pgvector, OpenAI's GPT-4, and the Mistral embedding model. Each piece of this puzzle plays a vital role: LlamaIndex helps you manage your data efficiently, Pgvector gives you lightning-fast access to your vectors, GPT-4 empowers your applications with natural language generation, and the Mistral embedding model provides rich representations of your data. Together, these tools form a seamless pipeline that allows you to retrieve and generate information with remarkable accuracy and efficiency.
But that’s not all! You've also had the chance to explore optimization tips that will enhance your RAG system's functionality and speed. Plus, our handy free RAG cost calculator gives you a clear view of your operational expenses, making it easier to budget for your projects. So, what’s next? The possibilities are endless! Dive into building, optimizing, and innovating your own RAG applications. Experiment, explore new features, and push the boundaries of what you’ve learned here. Go ahead, unleash your creativity, and transform your ideas into reality—your RAG adventure is just getting started!
Further Resources
🌟 In addition to this RAG tutorial, unleash your full potential with these incredible resources to level up your RAG skills.
- How to Build a Multimodal RAG | Documentation
- How to Enhance the Performance of Your RAG Pipeline
- Graph RAG with Milvus | Documentation
- How to Evaluate RAG Applications - Zilliz Learn
- Generative AI Resource Hub | Zilliz
We'd Love to Hear What You Think!
We’d love to hear your thoughts! 🌟 Leave your questions or comments below or join our vibrant Milvus Discord community to share your experiences, ask questions, or connect with thousands of AI enthusiasts. Your journey matters to us!
If you like this tutorial, show your support by giving our Milvus GitHub repo a star ⭐—it means the world to us and inspires us to keep creating! 💖
- Introduction to RAG
- Key Components We'll Use for This RAG Chatbot
- Step 1: Install and Set Up Llamaindex
- Step 2: Install and Set Up OpenAI GPT-o1
- Step 3: Install and Set Up Mistral Embed
- Step 4: Install and Set Up Pgvector
- Step 5: Build a RAG Chatbot
- Optimization Tips
- RAG Cost Calculator: A Free Tool to Calculate Your Cost in Seconds
- What Have You Learned?
- Further Resources
- We'd Love to Hear What You Think!
Content
Vector Database at Scale
Zilliz Cloud is a fully-managed vector database built for scale, perfect for your RAG apps.
Try Zilliz Cloud for Free


