Build RAG Chatbot with Haystack, OpenSearch, STACKIT E5-mistral-7b-instruct, and AmazonBedrock titan-embed-text-v1
Introduction to RAG
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a game-changer for GenAI applications, especially in conversational AI. It combines the power of pre-trained large language models (LLMs) like OpenAI’s GPT with external knowledge sources stored in vector databases such as Milvus and Zilliz Cloud, allowing for more accurate, contextually relevant, and up-to-date response generation. A RAG pipeline usually consists of four basic components: a vector database, an embedding model, an LLM, and a framework.
Key Components We'll Use for This RAG Chatbot
This tutorial shows you how to build a simple RAG chatbot in Python using the following components:
- Haystack: An open-source Python framework designed for building production-ready NLP applications, particularly question answering and semantic search systems. Haystack excels at retrieving information from large document collections through its modular architecture that combines retrieval and reader components. Ideal for developers creating search applications, chatbots, and knowledge management systems that require efficient document processing and accurate information extraction from unstructured text.
- OpenSearch: An open-source search and analytics suite derived from Elasticsearch. It offers robust full-text search and real-time analytics, with vector search available as an add-on for similarity-based queries, extending its capabilities to handle high-dimensional data. Since it is just a vector search add-on rather than a purpose-built vector database, it lacks scalability and availability and many other advanced features required by enterprise-level applications. Therefore, if you prefer a much more scalable solution or hate to manage your own infrastructure, we recommend using Zilliz Cloud, which is a fully managed vector database service built on the open-source Milvus and offers a free tier supporting up to 1 million vectors.)
- STACKIT E5-mistral-7b-instruct: A 7B-parameter instruction-tuned language model optimized for task-specific guidance and multi-turn dialogue. It excels in understanding complex prompts, generating coherent responses, and adapting to diverse applications like chatbots, automation, and content creation. Ideal for developers seeking efficient, scalable AI solutions with minimal computational overhead.
- AmazonBedrock Titan-Embed-Text-v1: A high-performance embedding model designed to convert text into dense vector representations, enabling semantic search, clustering, and retrieval tasks. Strengths include scalability, multilingual support, and robust accuracy. Ideal for enterprise applications like recommendation systems, document similarity analysis, and AI-driven search engines within AWS environments.
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have a functional chatbot capable of answering questions based on a custom knowledge base.
Note: Since we may use proprietary models in our tutorials, make sure you have the required API key beforehand.
Step 1: Install and Set Up Haystack
import os
import requests
from haystack import Pipeline
from haystack.components.converters import MarkdownToDocument
from haystack.components.preprocessors import DocumentSplitter
from haystack.components.writers import DocumentWriter
Step 2: Install and Set Up STACKIT E5-mistral-7b-instruct
STACKIT is the cloud and colocation provider of the Schwarz Group. We can use different models on its cloud services with ease through its API.
pip install stackit-haystack
from haystack_integrations.components.generators.stackit import STACKITChatGenerator
from haystack.dataclasses import ChatMessage
generator = STACKITChatGenerator(model="intfloat/e5-mistral-7b-instruct")
Step 3: Install and Set Up AmazonBedrock titan-embed-text-v1
Amazon Bedrock is a fully managed service that makes high-performing foundation models from leading AI startups and Amazon available through a unified API.
To use embedding models on Amazon Bedrock for text and document embedding together with Haystack, you need to initialize an AmazonBedrockTextEmbedder and AmazonBedrockDocumentEmbedderwith the model name, the AWS credentials (aws_access_key_id, aws_secret_access_key, and aws_region_name) should be set as environment variables, be configured as described above or passed as Secret arguments. Note, make sure the region you set supports Amazon Bedrock.
Now, let's start installing and setting up models with Amazon Bedrock.
pip install amazon-bedrock-haystack
import os
from haystack_integrations.components.embedders.amazon_bedrock import AmazonBedrockTextEmbedder
from haystack_integrations.components.embedders.amazon_bedrock import AmazonBedrockDocumentEmbedder
from haystack.dataclasses import Document
os.environ["AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID"] = "..."
os.environ["AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY"] = "..."
os.environ["AWS_DEFAULT_REGION"] = "us-east-1" # just an example
text_embedder = AmazonBedrockTextEmbedder(model="amazon.titan-embed-text-v1",
input_type="search_query"
document_embedder = AmazonBedrockDocumentEmbedder(model="amazon.titan-embed-text-v1",
input_type="search_document"
Step 4: Install and Set Up OpenSearch
If you have Docker set up, we recommend pulling the Docker image and running it.
docker pull opensearchproject/opensearch:2.11.0
docker run -p 9200:9200 -p 9600:9600 -e "discovery.type=single-node" -e "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms1024m -Xmx1024m" opensearchproject/opensearch:2.11.0
Once you have a running OpenSearch instance, install the opensearch-haystack integration:
pip install opensearch-haystack
from haystack_integrations.components.retrievers.opensearch import OpenSearchEmbeddingRetriever
from haystack_integrations.document_stores.opensearch import OpenSearchDocumentStore
document_store = OpenSearchDocumentStore(hosts="http://localhost:9200", use_ssl=True,
verify_certs=False, http_auth=("admin", "admin"))
retriever = OpenSearchEmbeddingRetriever(document_store=document_store)
Step 5: Build a RAG Chatbot
Now that you’ve set up all components, let’s start to build a simple chatbot. We’ll use the Milvus introduction doc as a private knowledge base. You can replace it your own dataset to customize your RAG chatbot.
url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/milvus-io/milvus-docs/refs/heads/v2.5.x/site/en/about/overview.md'
example_file = 'example_file.md'
response = requests.get(url)
with open(example_file, 'wb') as f:
f.write(response.content)
file_paths = [example_file] # You can replace it with your own file paths.
indexing_pipeline = Pipeline()
indexing_pipeline.add_component("converter", MarkdownToDocument())
indexing_pipeline.add_component("splitter", DocumentSplitter(split_by="sentence", split_length=2))
indexing_pipeline.add_component("embedder", document_embedder)
indexing_pipeline.add_component("writer", DocumentWriter(document_store))
indexing_pipeline.connect("converter", "splitter")
indexing_pipeline.connect("splitter", "embedder")
indexing_pipeline.connect("embedder", "writer")
indexing_pipeline.run({"converter": {"sources": file_paths}})
# print("Number of documents:", document_store.count_documents())
question = "What is Milvus?" # You can replace it with your own question.
retrieval_pipeline = Pipeline()
retrieval_pipeline.add_component("embedder", text_embedder)
retrieval_pipeline.add_component("retriever", retriever)
retrieval_pipeline.connect("embedder", "retriever")
retrieval_results = retrieval_pipeline.run({"embedder": {"text": question}})
# for doc in retrieval_results["retriever"]["documents"]:
# print(doc.content)
# print("-" * 10)
from haystack.utils import Secret
from haystack.components.builders import PromptBuilder
retriever = OpenSearchEmbeddingRetriever(document_store=document_store)
text_embedder = AmazonBedrockTextEmbedder(model="amazon.titan-embed-text-v1",
input_type="search_query"
prompt_template = """Answer the following query based on the provided context. If the context does
not include an answer, reply with 'I don't know'.\n
Query: {{query}}
Documents:
{% for doc in documents %}
{{ doc.content }}
{% endfor %}
Answer:
"""
rag_pipeline = Pipeline()
rag_pipeline.add_component("text_embedder", text_embedder)
rag_pipeline.add_component("retriever", retriever)
rag_pipeline.add_component("prompt_builder", PromptBuilder(template=prompt_template))
rag_pipeline.add_component("generator", generator)
rag_pipeline.connect("text_embedder.embedding", "retriever.query_embedding")
rag_pipeline.connect("retriever.documents", "prompt_builder.documents")
rag_pipeline.connect("prompt_builder", "generator")
results = rag_pipeline.run({"text_embedder": {"text": question}, "prompt_builder": {"query": question},})
print('RAG answer:\n', results["generator"]["replies"][0])
Optimization Tips
As you build your RAG system, optimization is key to ensuring peak performance and efficiency. While setting up the components is an essential first step, fine-tuning each one will help you create a solution that works even better and scales seamlessly. In this section, we’ll share some practical tips for optimizing all these components, giving you the edge to build smarter, faster, and more responsive RAG applications.
Haystack optimization tips
To optimize Haystack in a RAG setup, ensure you use an efficient retriever like FAISS or Milvus for scalable and fast similarity searches. Fine-tune your document store settings, such as indexing strategies and storage backends, to balance speed and accuracy. Use batch processing for embedding generation to reduce latency and optimize API calls. Leverage Haystack's pipeline caching to avoid redundant computations, especially for frequently queried documents. Tune your reader model by selecting a lightweight yet accurate transformer-based model like DistilBERT to speed up response times. Implement query rewriting or filtering techniques to enhance retrieval quality, ensuring the most relevant documents are retrieved for generation. Finally, monitor system performance with Haystack’s built-in evaluation tools to iteratively refine your setup based on real-world query performance.
OpenSearch optimization tips
To optimize OpenSearch in a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) setup, fine-tune indexing by enabling efficient mappings and reducing unnecessary stored fields. Use HNSW for vector search to speed up similarity queries while balancing recall and latency with appropriate ef_search and ef_construction values. Leverage shard and replica settings to distribute load effectively, and enable caching for frequent queries. Optimize text-based retrieval with BM25 tuning and custom analyzers for better relevance. Regularly monitor cluster health, index size, and query performance using OpenSearch Dashboards and adjust configurations accordingly.
STACKIT E5-mistral-7b-instruct optimization tips
To optimize STACKIT E5-mistral-7b-instruct in RAG, fine-tune the model on domain-specific data to align embeddings with retrieval tasks. Use dynamic chunking (256-512 tokens) for balanced context retention and computational efficiency. Apply quantization (e.g., 4-bit) to reduce memory usage without significant accuracy loss. Leverage instruction prefixes like "Retrieve relevant info for:" to sharpen focus. Implement cache layers for repetitive queries and prune low-scoring retrieved documents pre-generation. Monitor latency and adjust temperature (0.1-0.3) to balance determinism and creativity. Prioritize GPU memory optimization via mixed precision and kernel fusion.
AmazonBedrock titan-embed-text-v1 optimization tips
To optimize titan-embed-text-v1 in a RAG setup, preprocess inputs by removing redundant whitespace and truncating excessively long texts to fit its 8K-token limit. Use batch embedding requests to reduce latency and costs. Fine-tune chunking strategies to balance context retention (e.g., 512-token segments) and avoid fragmentation. Normalize embeddings to improve retrieval accuracy. Leverage metadata filtering to refine retrieved results. Test newer model versions for performance gains. Cache frequent or repeated queries to minimize redundant computations. Monitor embedding quality via cosine similarity thresholds and adjust retrieval thresholds dynamically.
By implementing these tips across your components, you'll be able to enhance the performance and functionality of your RAG system, ensuring it’s optimized for both speed and accuracy. Keep testing, iterating, and refining your setup to stay ahead in the ever-evolving world of AI development.
RAG Cost Calculator: A Free Tool to Calculate Your Cost in Seconds
Estimating the cost of a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline involves analyzing expenses across vector storage, compute resources, and API usage. Key cost drivers include vector database queries, embedding generation, and LLM inference.
RAG Cost Calculator is a free tool that quickly estimates the cost of building a RAG pipeline, including chunking, embedding, vector storage/search, and LLM generation. It also helps you identify cost-saving opportunities and achieve up to 10x cost reduction on vector databases with the serverless option.
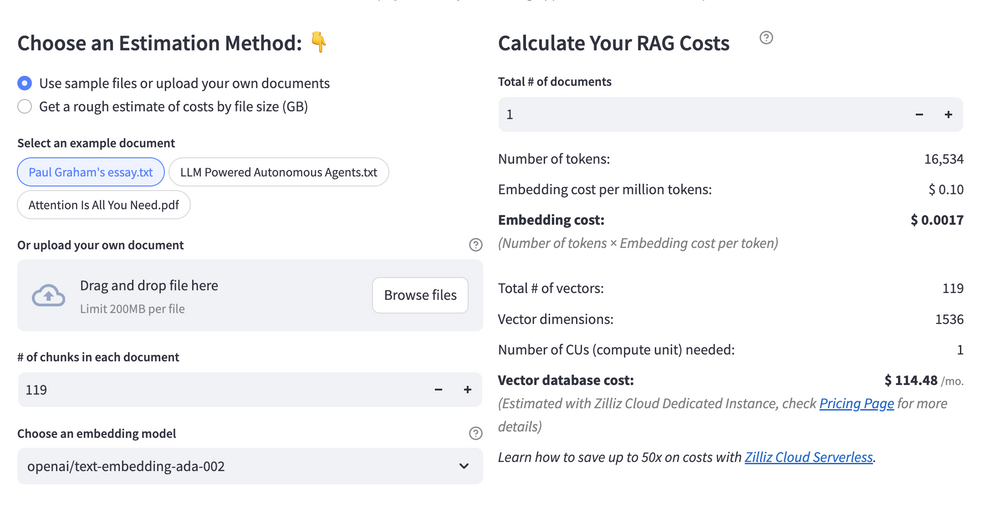 Calculate your RAG cost
Calculate your RAG cost
What Have You Learned?
By diving into this tutorial, you’ve unlocked the magic of building a powerful RAG system from the ground up! You’ve seen how Haystack acts as the backbone, seamlessly orchestrating the flow of data between components, while OpenSearch steps in as your trusty vector database, storing and retrieving embeddings with speed and precision. The STACKIT E5-mistral-7b-instruct model blew you away with its ability to generate human-like responses, and Amazon Bedrock’s Titan-embed-text-v1 showed off its knack for turning text into rich, meaningful vectors. Together, these pieces form a dynamic pipeline where Haystack’s flexibility, OpenSearch’s search power, Mistral’s creativity, and Titan’s accuracy work in harmony to deliver context-aware, intelligent answers. You’ve also picked up pro tips for optimization—like tuning chunk sizes and refining retrieval strategies—to squeeze every drop of performance from your system. And let’s not forget that handy free RAG cost calculator you explored, which helps you balance quality and budget like a pro!
Now, imagine the possibilities ahead. You’ve got the tools to build systems that answer questions, summarize content, or even power chatbots that feel alive. Whether you’re enhancing customer support, revolutionizing research, or creating something entirely new, your journey is just beginning. So fire up your IDE, experiment with those optimizations, and let your creativity run wild. The world of RAG is yours to shape—go build something amazing, share your wins, and keep pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. The future is waiting, and you’re already crushing it! 🚀
Further Resources
🌟 In addition to this RAG tutorial, unleash your full potential with these incredible resources to level up your RAG skills.
- How to Build a Multimodal RAG | Documentation
- How to Enhance the Performance of Your RAG Pipeline
- Graph RAG with Milvus | Documentation
- How to Evaluate RAG Applications - Zilliz Learn
- Generative AI Resource Hub | Zilliz
We'd Love to Hear What You Think!
We’d love to hear your thoughts! 🌟 Leave your questions or comments below or join our vibrant Milvus Discord community to share your experiences, ask questions, or connect with thousands of AI enthusiasts. Your journey matters to us!
If you like this tutorial, show your support by giving our Milvus GitHub repo a star ⭐—it means the world to us and inspires us to keep creating! 💖
- Introduction to RAG
- Key Components We'll Use for This RAG Chatbot
- Step 1: Install and Set Up Haystack
- Step 2: Install and Set Up STACKIT E5-mistral-7b-instruct
- Step 3: Install and Set Up AmazonBedrock titan-embed-text-v1
- Step 4: Install and Set Up OpenSearch
- Step 5: Build a RAG Chatbot
- Optimization Tips
- RAG Cost Calculator: A Free Tool to Calculate Your Cost in Seconds
- What Have You Learned?
- Further Resources
- We'd Love to Hear What You Think!
Content
Vector Database at Scale
Zilliz Cloud is a fully-managed vector database built for scale, perfect for your RAG apps.
Try Zilliz Cloud for Free


