Making With Milvus: AI-Infused Proptech for Personalized Real Estate Search

Artificial intelligence (AI) has powerful applications in real estate that are transforming the home search process. Tech savvy real estate professionals have been taking advantage of AI for years, recognizing its ability to help clients find the right home faster and simplify the process of purchasing property. The coronavirus pandemic has accelerated interest, adoption, and investement in property technology (or proptech) worldwide, suggesting it will play an increasingly greater role in the real estate industry moving forward.
This article explores how Beike used vector similarity search to build a house hunting platform that provides personalized results and recommends listings in near real-time.
Jump to:
What is vector similarity search?
Vector similarity search has applications spanning a wide variety of artificial intelligence, deep learning, and traditional vector calculation scenarios. The proliferation of AI technology is in part attributed to vector search and its ability to make sense of unstructured data, which includes things like images, video, audio, behavior data, documents, and much more.
Unstructured data makes up an estimated 80-90% of all data, and extracting insights from it is quickly becoming a requirement for businesses that want to remain competitive in an ever-changing world. Increasing demand for unstructured data analytics, rising compute power, and declining compute costs have made AI-enabled vector search more accessible than ever.
 Understanding the difference between structured and unstructured data.
Understanding the difference between structured and unstructured data.
Traditionally, unstructured data has been a challenge to process and analyze at scale because it doesn't follow a predefined model or organizational structure. Neural networks (e.g., CNN, RNN, and BERT) make it possible to convert unstructured data into feature vectors, a numerical data format that can be easily interpreted by computers. Algorithms are then used to calculate similarity between vectors using metrics like cosine similarity or Euclidean distance.
Ultimately, vector similarity search is a broad term that desribes techniques for identifying similar things in massive datasets. Beike uses this technology to power an intelligent home search engine that automatically recommends listings based on individual user preferences, search history, and property criteria—accelerating the real estate search and purchase process. Milvus is an open-source vector database that connects information with algorithms, enabling Beike to develop and manage its AI real estate platform.
How does Milvus manage vector data?
Milvus was built specifically for large-scale vector data management, and has applications spanning image and video search, chemical similarity analysis, personalized recommendation systems, conversational AI, and much more. Vector datasets stored in Milvus can be efficiently queried, with most implementations following this general process:
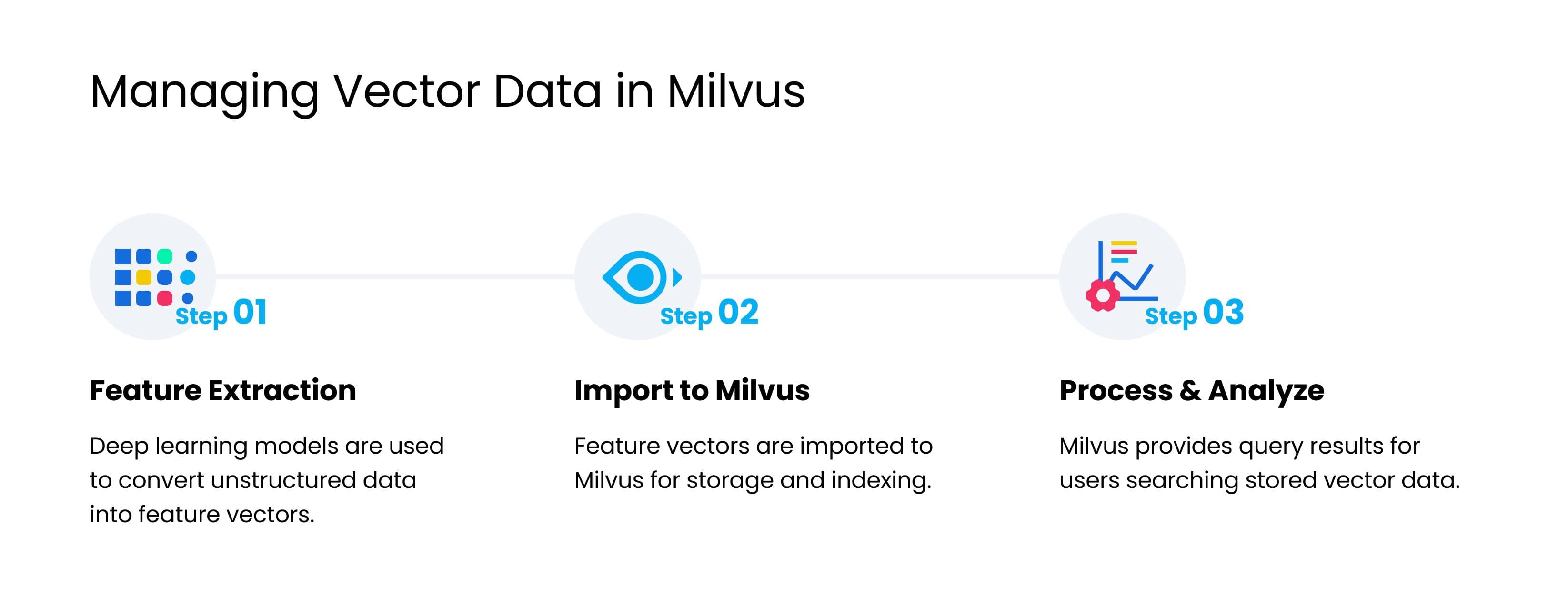 How does Milvus manage vector data?
How does Milvus manage vector data?
How does Beike use Milvus to make house hunting smarter?
Commonly described as China's answer to Zillow, Beike is an online platform that allows real estate agents to list properties for rent or sale. To help improve the home search experience for house hunters, and to help agents close deals faster, the company built an AI-powered search engine for its listing database. Beike’s real estate listing database was converted into feature vectors then fed into Milvus for indexing and storage. Milvus is then used to conduct similarity search based on an input listing, search criteria, user profile, or other criteria.
For example, when searching for more homes similar to a given listing, features such as floor plan, size, orientation, interior finishings, paint colors, and more are extracted. Since the original database of property listings listing data has been indexed, searches can be conducted in mere milliseconds. Beike’s final product had an average query time of 113 milliseconds on a dataset containing over 3 million vectors. However, Milvus is capable of maintaining efficient speeds on trillion-scale datasets—making light work of this relatively small real estate database. In general, the system follows the following process:
Deep learning models (e.g., CNN, RNN, or BERT) convert unstructured data to feature vectors, which are then imported to Milvus.
Milvus stores and indexes the feature vectors.
Milvus returns similarity search results based on user queries.
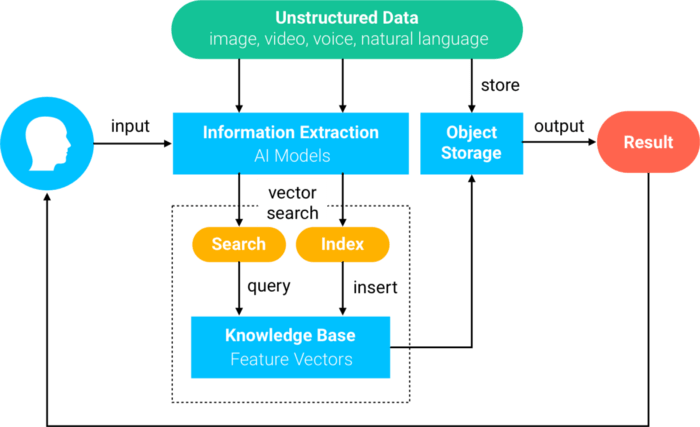 An overview of Milvus.
An overview of Milvus.
Beike’s intelligent real estate search platform is powered by a recommendation algorithm that calculates vector similarity using cosine distance. The system finds similar homes based on favorite listings and search criteria. At a high level, it works as follows:
Based on an input listing, characteristics such as floor plan, size, and orientation are used to extract 4 collections of feature vectors.
The extracted feature collections are used to perform similarity search in Milvus. Results of the query for each collection of vectors are a measure of similarity between the input listing and other similar listings.
The search results from each of the 4 vector collections are compared then used to recommend similar homes.
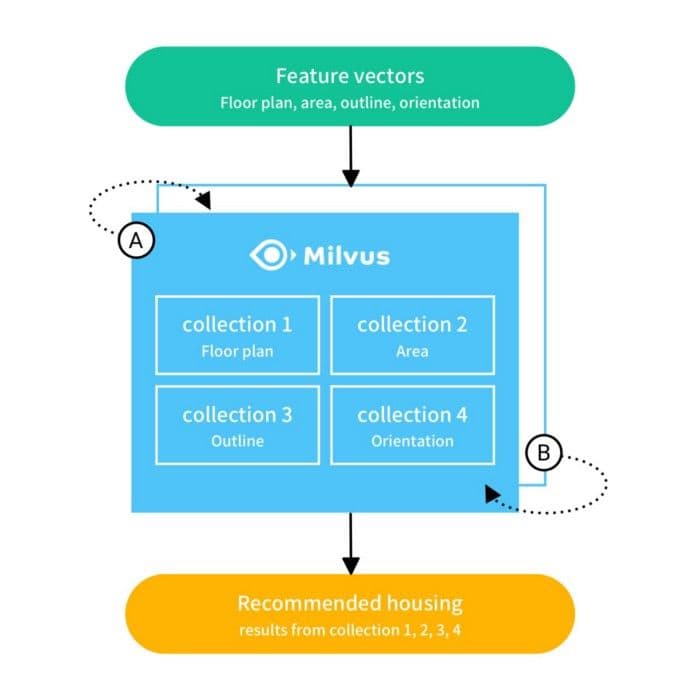 An overview of Beike’s intelligent house hunting platform.
An overview of Beike’s intelligent house hunting platform.
As the figure above shows, the system implements an A/B table switching mechanism for updating data. Milvus stores the data for the first T days in table A, on day T+1 it starts to store data in table B, on day 2T+1, it starts to rewrite table A, and so forth.
To learn more about making things with Milvus, check out the following resources:
Start Free, Scale Easily
Try the fully-managed vector database built for your GenAI applications.
Try Zilliz Cloud for FreeKeep Reading

How to Install and Run OpenClaw (Previously Clawdbot/Moltbot) on Mac
Turn your Mac into an AI gateway for WhatsApp, Telegram, Discord, iMessage, and more — in under 5 minutes.

8 Latest RAG Advancements Every Developer Should Know
Explore eight advanced RAG variants that can solve real problems you might be facing: slow retrieval, poor context understanding, multimodal data handling, and resource optimization.

Similarity Metrics for Vector Search
Exploring five similarity metrics for vector search: L2 or Euclidean distance, cosine distance, inner product, and hamming distance.
