Making with Milvus: AI-Powered News Recommendation Inside Xiaomi's Mobile Browser

From social media feeds to playlist recommendations on Spotify, artificial intelligence already plays a major role in the content we see and interact with each day. In an effort to differentiate their mobile web browser, multinational electronics manufacturer Xiaomi built an AI-powered news recommendation engine. Milvus, an open-source vector database built specifically for similarity search and artificial intelligence, was used as the application’s core data management platform. This article explains how Xiaomi built its AI-powered news recommendation engine, and how Milvus and other AI algorithms were used.
Using AI to suggest personalized content and cut through news noise
With the New York Times alone publishing over 230 pieces of content each day, the sheer volume of articles produced makes it impossible for individuals to get a comprehensive view of all the news. To help sift through large volumes of content, and recommend the most relevant or interesting pieces, we increasingly turn to AI. Although recommendations remain far from perfect, machine learning is increasingly necessary to cut through the constant stream of new information pouring out of our increasingly complex and interconnected world.
Xiaomi makes and invests in smartphones, mobile apps, laptops, home appliances, and many more products. In an effort to differentiate a mobile browser that comes preinstalled on many of 40+ million smartphones the company sells each quarter, Xiaomi built a news recommendation system into it. When users launch Xiaomi’s mobile browser, artificial intelligence is used to recommend similar content based on user search history, interests, and more. Milvus is an open-source vector similarity search database used to accelerate retrieval of related articles.
How does AI-powered content recommendation work?
At its core, news recommendation (or any other type of content recommendation system) involves comparing input data to a massive database to find similar information. Successful content recommendation involves balancing relevance with timeliness, and efficiently incorporating huge volumes of new data—often in real time.
To accommodate massive datasets, recommendation systems are typically divided into two stages:
- Retrieval: During retrieval, content is narrowed down from the broader library based on user interests and behavior. In Xiaomi’s mobile browser, thousands of pieces of content are selected from a massive dataset that contains millions of news articles.
- Sorting: Next, content selected during retrieval is sorted according to certain indicators before being pushed to the user. As users engage with recommended content, the system adapts in real time to provide more relevant suggestions.
News content recommendations need to be made in real-time based on user behavior and recently published content. Additionally, suggested content must match user interests and search intent as much as possible.
Milvus + BERT = intelligent content suggestions
Milvus is an open-source vector similarity search database that can be integrated with deep learning models to power applications spanning natural language processing, identity verification, and much more. Milvus indexes large vector datasets to make search more efficient, and supports a variety of popular AI frameworks to simplify the process of developing machine learning applications. These characteristics make the platform the ideal for storing and querying vector data, a critical component of many machine learning applications.
Xiaomi selected Milvus to manage vector data for its intelligent news recommendation system because it is fast, reliable, and requires minimal configuration and maintenance. However, Milvus must be paired with an AI algorithm to build deployable applications. Xiaomi selected BERT, short for Bidirectional Encoder Representation Transformers, as the language representation model in its recommendation engine. BERT can be used as a general NLU (natural language understanding) model that can drive a number of different NLP (natural language processing) tasks. Its key features include:
- BERT’s transformer is used as the main framework of the algorithm and is capable of capturing explicit and implicit relationships within and between sentences.
- Multi-task learning goals, masked language modeling (MLM), and next sentence prediction (NSP).
- BERT performs better with greater amounts of data, and can enhance other natural language processing techniques such as Word2Vec by acting as a conversion matrix.
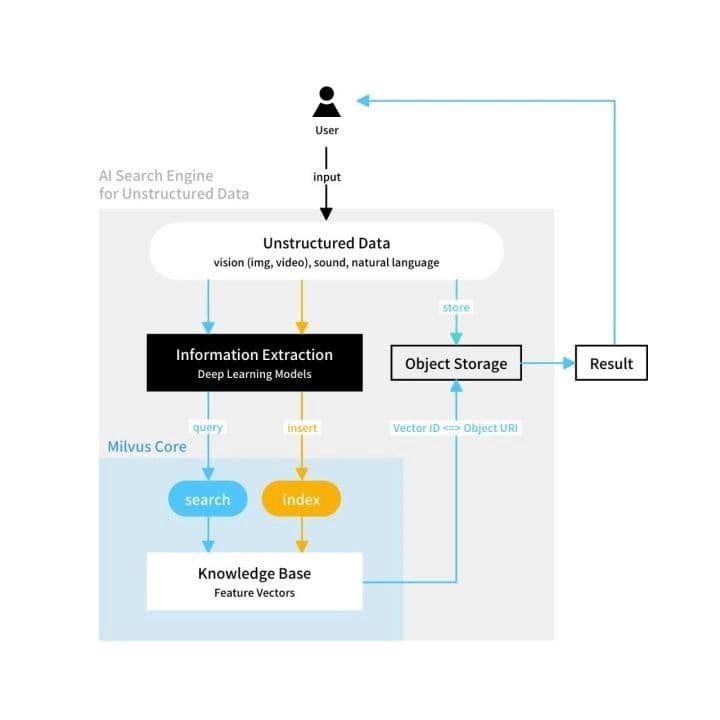 Milvus working with BERT.
Milvus working with BERT.
BERT’s network architecture uses a multi-layer transformer structure that abandons the traditional RNN and CNN neural networks. It works by converting the distance between two words at any position into one through its attention mechanism, and solves the dependency issue that has persisted in NLP for some time.
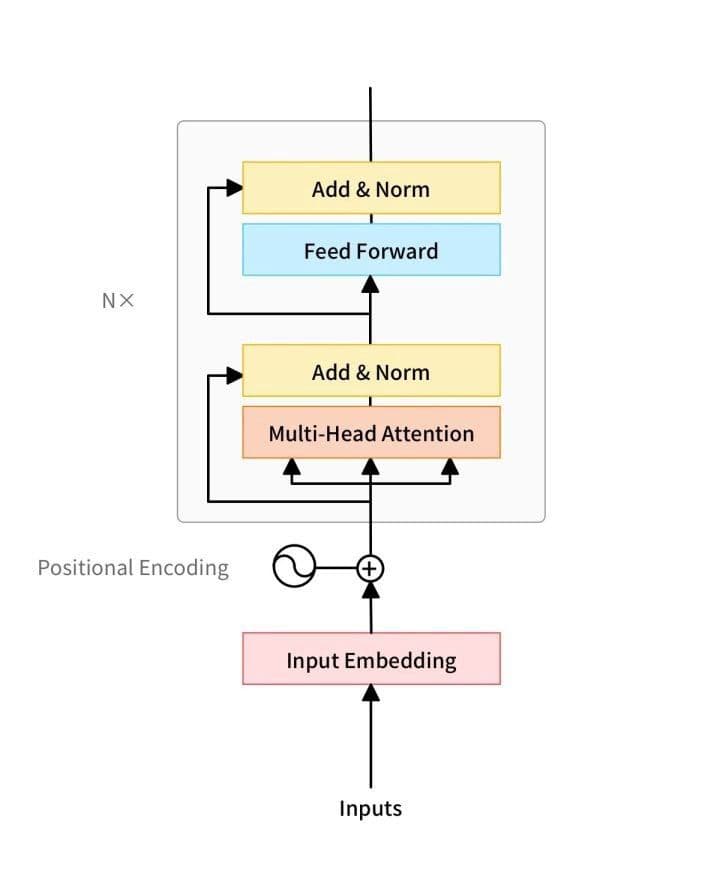 A transformer’s network architecture in BERT.
A transformer’s network architecture in BERT.
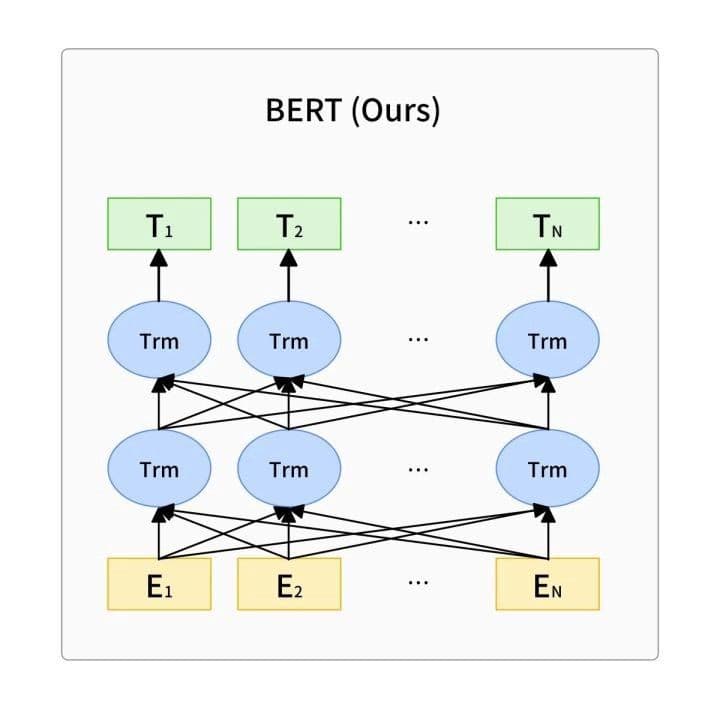 BERT’s network structure. ‘Trm’ represents the transformer network architecture depicted above.
BERT’s network structure. ‘Trm’ represents the transformer network architecture depicted above.
BERT provides a simple and a complex model. The corresponding hyperparameters are as follows: BERT BASE: L = 12, H = 768, A = 12, total parameter 110M; BERT LARGE: L = 24, H = 1024, A = 16, the total number of parameters is 340M.
In the above hyperparameters, L represents the number of layers in the network (i.e. the number of Transformer blocks), A represents the number of self-Attention in Multi-Head Attention, and the filter size is 4H.
Xiaomi’s content recommendation system
Xiaomi browser-based news recommender system relies on three key components: vectorization, ID mapping, and approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) service.
Vectorization is process where article titles are converted into general sentence vectors. The SimBert model, based on BERT, is used in Xiaomi’s recommendation system. SimBert is a 12-layer model with a hidden size of 768. Simbert uses the training model Chinese L-12_H-768_A-12 for continuous training (training task being “metric learning +UniLM”, and has trained 1.17 million steps on a signle TITAN RTX with the Adam optimizer (learning rate 2e-6, batch size 128). Simply put, this is an optimized BERT model.
ANN algorithms compare vectorized article titles to the entire news library stored in Milvus, then return similar content for users. ID mapping is used to obtain relevant information such as page views and clicks for corresponding articles.
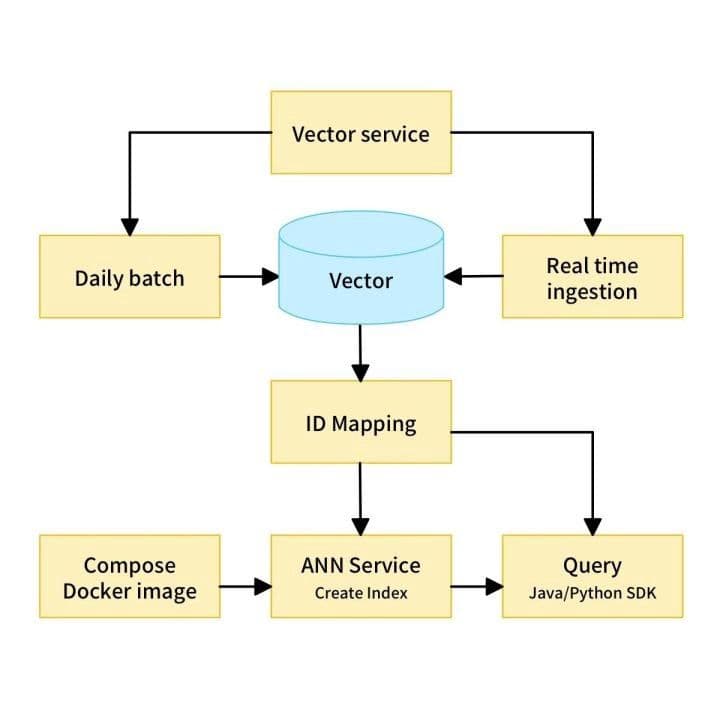 How content recommendation works.
How content recommendation works.
The data stored in Milvus that powers Xiaomi’s news recommendation engine is constantly being updated, including additional articles and activity information. As the system incorporates new data, old data must be purged. In this system, full data updates are done for the first T-1 days and incremental updates are done in the subsequent T days.
At defined intervals, old data is deleted and processed data of the T-1 days is inserted into the collection. Here newly generated data is incorporated in real time. Once new data is inserted, similarity search is conducted in Milvus. Retrieved articles are again sorted by click rate and other factors, and the top content is shown to users. In a scenario like this where data is frequently updated and results must be delivered in real time, Milvus' ability to rapidly incorporate and search new data makes it possible to drastically accelerate news content recommendation in Xiaomi’s mobile browser.
Milvus makes vector similarity search better
Vectorizing data and then calculating similarity between vectors is the most commonly used retrieval technology. The rise of ANN-based vector similarity search engines has greatly improved the efficiency of vector similarity calculations. Compared with similar solutions, Milvus offers optimized data storage, abundant SDKs, and a distributed version that greatly reduces the workload of building a retrieval layer. Additionally, Milvus' active open-source community is a powerful resource that can help answer questions and troubleshoot problems as they arise.
If you would like to learn more about vector similarity search and Milvus, check out the following resources:
- Check out Milvus on Github.
- Vector Similarity Search Hides in Plain View
- Accelerating Similarity Search on Really Big Data with Vector Indexing
Read other user stories to learn more about making things with Milvus.
Start Free, Scale Easily
Try the fully-managed vector database built for your GenAI applications.
Try Zilliz Cloud for FreeKeep Reading

Legal Document Analysis: Harnessing Zilliz Cloud's Semantic Search and RAG for Legal Insights
Zilliz Cloud transforms legal document analysis with AI-driven Semantic Search and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). By combining keyword and vector search, it enables faster, more accurate contract analysis, case law research, and regulatory tracking.

AI Integration in Video Surveillance Tools: Transforming the Industry with Vector Databases
Discover how AI and vector databases are revolutionizing video surveillance with real-time analysis, faster threat detection, and intelligent search capabilities for enhanced security.

Why Deepseek is Waking up AI Giants Like OpenAI And Why You Should Care
Discover how DeepSeek R1's open-source AI model with superior reasoning capabilities and lower costs is disrupting the AI landscape and challenging tech giants like OpenAI.
