Build RAG Chatbot with Haystack, Milvus, OpenAI GPT-o3-mini, and OpenAI text-embedding-3-small
Introduction to RAG
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a game-changer for GenAI applications, especially in conversational AI. It combines the power of pre-trained large language models (LLMs) like OpenAI’s GPT with external knowledge sources stored in vector databases such as Milvus and Zilliz Cloud, allowing for more accurate, contextually relevant, and up-to-date response generation. A RAG pipeline usually consists of four basic components: a vector database, an embedding model, an LLM, and a framework.
Key Components We'll Use for This RAG Chatbot
This tutorial shows you how to build a simple RAG chatbot in Python using the following components:
- Haystack: An open-source Python framework designed for building production-ready NLP applications, particularly question answering and semantic search systems. Haystack excels at retrieving information from large document collections through its modular architecture that combines retrieval and reader components. Ideal for developers creating search applications, chatbots, and knowledge management systems that require efficient document processing and accurate information extraction from unstructured text.
- Milvus: An open-source vector database optimized to store, index, and search large-scale vector embeddings efficiently, perfect for use cases like RAG, semantic search, and recommender systems. If you hate to manage your own infrastructure, we recommend using Zilliz Cloud, which is a fully managed vector database service built on Milvus and offers a free tier supporting up to 1 million vectors.
- OpenAI GPT-o3-mini: A lightweight, efficient language model optimized for rapid text generation and comprehension. Designed to balance performance with resource efficiency, it excels in applications requiring quick responses and lower computational costs, such as mobile apps, customer service chatbots, and real-time content moderation. Ideal for developers seeking scalable AI solutions with minimal infrastructure demands.
- OpenAI text-embedding-3-small: Designed to generate dense vector representations of text, this model excels in efficiency and cost-effectiveness, optimized for speed and low resource usage. It delivers competitive performance in semantic similarity, retrieval, and clustering tasks, making it ideal for large-scale applications like search engines, recommendation systems, and text classification where balancing accuracy with computational cost is crucial.
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have a functional chatbot capable of answering questions based on a custom knowledge base.
Note: Since we may use proprietary models in our tutorials, make sure you have the required API key beforehand.
Step 1: Install and Set Up Haystack
import os
import requests
from haystack import Pipeline
from haystack.components.converters import MarkdownToDocument
from haystack.components.preprocessors import DocumentSplitter
from haystack.components.writers import DocumentWriter
Step 2: Install and Set Up OpenAI GPT-o3-mini
To use OpenAI models, you need to get an OpenAI API key. The Haystack integration with OpenAI models uses an OPENAI_API_KEY environment variable by default. Otherwise, you can pass an API key at initialization with api_key:
generator = OpenAIGenerator(api_key=Secret.from_token("<your-api-key>"), model="gpt-4o-mini")
Then, the generator component needs a prompt to operate, but you can pass any text generation parameters valid for the openai.ChatCompletion.create method directly to this component using the generation_kwargs parameter, both at initialization and to run() method. For more details on the parameters supported by the OpenAI API, refer to the OpenAI documentation.
Now let's install and set up OpenAI models.
from haystack.components.generators import OpenAIGenerator
generator = OpenAIGenerator(model="o3-mini", api_key=Secret.from_token("<your-api-key>"))
Step 3: Install and Set Up OpenAI text-embedding-3-small
Text documents often come with a set of metadata. If they are distinctive and semantically meaningful, you can embed them along with the text of the document to improve retrieval.
from haystack import Document
from haystack.components.embedders import OpenAIDocumentEmbedder
doc = Document(content="some text",meta={"title": "relevant title", "page number": 18})
document_embedder = OpenAIDocumentEmbedder(meta_fields_to_embed=["title"])
docs_w_embeddings = embedder.run(documents=[doc])["documents"]
Now let's install and set up the model.
from haystack import Document
from haystack.components.embedders import OpenAIDocumentEmbedder
from haystack.components.embedders import OpenAITextEmbedder
text_embedder = OpenAITextEmbedder(api_key=Secret.from_token("<your-api-key>"), model="text-embedding-3-small")
document_embedder = OpenAIDocumentEmbedder(api_key=Secret.from_token("<your-api-key>"), model="text-embedding-3-small")
Step 4: Install and Set Up Milvus
pip install --upgrade pymilvus milvus-haystack
from milvus_haystack import MilvusDocumentStore
from milvus_haystack.milvus_embedding_retriever import MilvusEmbeddingRetriever
document_store = MilvusDocumentStore(connection_args={"uri": "./milvus.db"}, drop_old=True,)
retriever = MilvusEmbeddingRetriever(document_store=document_store, top_k=3)
Step 5: Build a RAG Chatbot
Now that you’ve set up all components, let’s start to build a simple chatbot. We’ll use the Milvus introduction doc as a private knowledge base. You can replace it your own dataset to customize your RAG chatbot.
url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/milvus-io/milvus-docs/refs/heads/v2.5.x/site/en/about/overview.md'
example_file = 'example_file.md'
response = requests.get(url)
with open(example_file, 'wb') as f:
f.write(response.content)
file_paths = [example_file] # You can replace it with your own file paths.
indexing_pipeline = Pipeline()
indexing_pipeline.add_component("converter", MarkdownToDocument())
indexing_pipeline.add_component("splitter", DocumentSplitter(split_by="sentence", split_length=2))
indexing_pipeline.add_component("embedder", document_embedder)
indexing_pipeline.add_component("writer", DocumentWriter(document_store))
indexing_pipeline.connect("converter", "splitter")
indexing_pipeline.connect("splitter", "embedder")
indexing_pipeline.connect("embedder", "writer")
indexing_pipeline.run({"converter": {"sources": file_paths}})
# print("Number of documents:", document_store.count_documents())
question = "What is Milvus?" # You can replace it with your own question.
retrieval_pipeline = Pipeline()
retrieval_pipeline.add_component("embedder", text_embedder)
retrieval_pipeline.add_component("retriever", retriever)
retrieval_pipeline.connect("embedder", "retriever")
retrieval_results = retrieval_pipeline.run({"embedder": {"text": question}})
# for doc in retrieval_results["retriever"]["documents"]:
# print(doc.content)
# print("-" * 10)
from haystack.utils import Secret
from haystack.components.builders import PromptBuilder
retriever = MilvusEmbeddingRetriever(document_store=document_store, top_k=3)
text_embedder = OpenAITextEmbedder(api_key=Secret.from_token("<your-api-key>"), model="text-embedding-3-small")
prompt_template = """Answer the following query based on the provided context. If the context does
not include an answer, reply with 'I don't know'.\n
Query: {{query}}
Documents:
{% for doc in documents %}
{{ doc.content }}
{% endfor %}
Answer:
"""
rag_pipeline = Pipeline()
rag_pipeline.add_component("text_embedder", text_embedder)
rag_pipeline.add_component("retriever", retriever)
rag_pipeline.add_component("prompt_builder", PromptBuilder(template=prompt_template))
rag_pipeline.add_component("generator", generator)
rag_pipeline.connect("text_embedder.embedding", "retriever.query_embedding")
rag_pipeline.connect("retriever.documents", "prompt_builder.documents")
rag_pipeline.connect("prompt_builder", "generator")
results = rag_pipeline.run({"text_embedder": {"text": question}, "prompt_builder": {"query": question},})
print('RAG answer:\n', results["generator"]["replies"][0])
Optimization Tips
As you build your RAG system, optimization is key to ensuring peak performance and efficiency. While setting up the components is an essential first step, fine-tuning each one will help you create a solution that works even better and scales seamlessly. In this section, we’ll share some practical tips for optimizing all these components, giving you the edge to build smarter, faster, and more responsive RAG applications.
Haystack optimization tips
To optimize Haystack in a RAG setup, ensure you use an efficient retriever like FAISS or Milvus for scalable and fast similarity searches. Fine-tune your document store settings, such as indexing strategies and storage backends, to balance speed and accuracy. Use batch processing for embedding generation to reduce latency and optimize API calls. Leverage Haystack's pipeline caching to avoid redundant computations, especially for frequently queried documents. Tune your reader model by selecting a lightweight yet accurate transformer-based model like DistilBERT to speed up response times. Implement query rewriting or filtering techniques to enhance retrieval quality, ensuring the most relevant documents are retrieved for generation. Finally, monitor system performance with Haystack’s built-in evaluation tools to iteratively refine your setup based on real-world query performance.
Milvus optimization tips
Milvus serves as a highly efficient vector database, critical for retrieval tasks in a RAG system. To optimize its performance, ensure that indexes are properly built to balance speed and accuracy; consider utilizing HNSW (Hierarchical Navigable Small World) for efficient nearest neighbor search where response time is crucial. Partitioning data based on usage patterns can enhance query performance and reduce load times, enabling better scalability. Regularly monitor and adjust cache settings based on query frequency to avoid latency during data retrieval. Employ batch processing for vector insertions, which can minimize database lock contention and enhance overall throughput. Additionally, fine-tune the model parameters by experimenting with the dimensionality of the vectors; higher dimensions can improve retrieval accuracy but may increase search time, necessitating a balance tailored to your specific use case and hardware infrastructure.
OpenAI GPT-3-mini optimization tips
Optimize OpenAI GPT-3-mini in RAG by chunking input data into smaller, semantically coherent segments to reduce token waste and improve retrieval relevance. Use structured prompts with explicit instructions (e.g., "Answer based on: [context]") to guide outputs. Fine-tune temperature (0.2-0.5 for precision) and max tokens to balance brevity and completeness. Cache frequent queries to reduce latency and costs. Preprocess retrieved documents to remove redundancy and align with query intent. Monitor outputs via metrics like BLEU or ROUGE and iterate based on user feedback.
OpenAI text-embedding-3-small optimization tips
Optimize input text by truncating or chunking to stay within the 8191-token limit while preserving semantic context. Normalize embeddings to unit vectors to improve cosine similarity accuracy. Batch embedding requests to reduce API calls and latency. Experiment with dimensionality reduction (e.g., 256-dim) to balance performance and storage costs. Preprocess text by removing redundant or noisy content and standardizing formats (lowercase, trimming whitespace). Cache frequent or static embeddings to avoid redundant computations. Monitor retrieval quality via metrics like recall@k and adjust chunking strategies or hybrid retrieval methods if needed. Fine-tune temperature and top-k parameters during generation to align with embedding outputs.
By implementing these tips across your components, you'll be able to enhance the performance and functionality of your RAG system, ensuring it’s optimized for both speed and accuracy. Keep testing, iterating, and refining your setup to stay ahead in the ever-evolving world of AI development.
RAG Cost Calculator: A Free Tool to Calculate Your Cost in Seconds
Estimating the cost of a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline involves analyzing expenses across vector storage, compute resources, and API usage. Key cost drivers include vector database queries, embedding generation, and LLM inference.
RAG Cost Calculator is a free tool that quickly estimates the cost of building a RAG pipeline, including chunking, embedding, vector storage/search, and LLM generation. It also helps you identify cost-saving opportunities and achieve up to 10x cost reduction on vector databases with the serverless option.
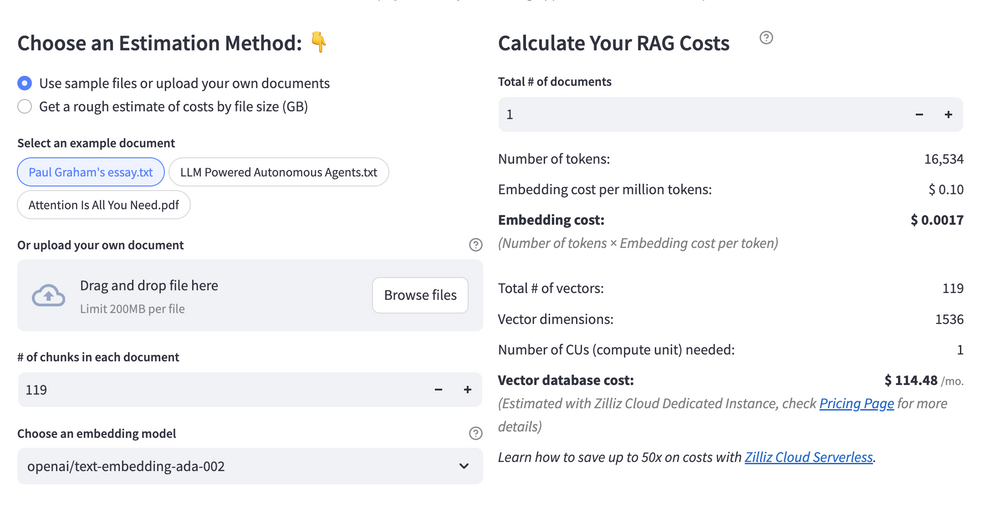 Calculate your RAG cost
Calculate your RAG cost
What Have You Learned?
By diving into this tutorial, you’ve unlocked the power of combining cutting-edge tools to build a fully functional RAG system! You learned how Haystack acts as the backbone, seamlessly orchestrating the flow of data between components. With Milvus as your vector database, you can efficiently store and retrieve embeddings at scale, ensuring lightning-fast similarity searches. The OpenAI text-embedding-3-small model transformed raw text into rich numerical representations, capturing semantic meaning in a way that makes retrieval precise and context-aware. Then, OpenAI’s GPT-3.5-turbo stepped in as the LLM powerhouse, generating human-like responses by synthesizing retrieved information into coherent, natural language answers. Together, these tools create a dynamic pipeline where data ingestion, embedding, retrieval, and generation work in harmony—turning unstructured information into actionable insights!
But this tutorial didn’t stop at the basics! You also explored pro tips for optimizing your RAG system, like tuning chunk sizes for embeddings or balancing speed and accuracy in Milvus configurations. Plus, the free RAG cost calculator gave you a practical way to estimate expenses and scale your projects smartly. Imagine what’s next: customizing this pipeline for your own datasets, experimenting with hybrid search strategies, or even fine-tuning models for domain-specific tasks. The skills you’ve gained here are a launchpad—whether you’re building chatbots, research tools, or enterprise-grade knowledge bases. So go ahead—fire up your IDE, tweak those parameters, and start creating! The future of AI-powered applications is yours to shape, one query at a time. Let’s build something amazing! 🚀
Further Resources
🌟 In addition to this RAG tutorial, unleash your full potential with these incredible resources to level up your RAG skills.
- How to Build a Multimodal RAG | Documentation
- How to Enhance the Performance of Your RAG Pipeline
- Graph RAG with Milvus | Documentation
- How to Evaluate RAG Applications - Zilliz Learn
- Generative AI Resource Hub | Zilliz
We'd Love to Hear What You Think!
We’d love to hear your thoughts! 🌟 Leave your questions or comments below or join our vibrant Milvus Discord community to share your experiences, ask questions, or connect with thousands of AI enthusiasts. Your journey matters to us!
If you like this tutorial, show your support by giving our Milvus GitHub repo a star ⭐—it means the world to us and inspires us to keep creating! 💖
- Introduction to RAG
- Key Components We'll Use for This RAG Chatbot
- Step 1: Install and Set Up Haystack
- Step 2: Install and Set Up OpenAI GPT-o3-mini
- Step 3: Install and Set Up OpenAI text-embedding-3-small
- Step 4: Install and Set Up Milvus
- Step 5: Build a RAG Chatbot
- Optimization Tips
- RAG Cost Calculator: A Free Tool to Calculate Your Cost in Seconds
- What Have You Learned?
- Further Resources
- We'd Love to Hear What You Think!
Content
Vector Database at Scale
Zilliz Cloud is a fully-managed vector database built for scale, perfect for your RAG apps.
Try Zilliz Cloud for Free


