Build RAG Chatbot with Haystack, Haystack In-memory store, Cohere Command R+, and OpenAI text-embedding-ada-002
Introduction to RAG
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a game-changer for GenAI applications, especially in conversational AI. It combines the power of pre-trained large language models (LLMs) like OpenAI’s GPT with external knowledge sources stored in vector databases such as Milvus and Zilliz Cloud, allowing for more accurate, contextually relevant, and up-to-date response generation. A RAG pipeline usually consists of four basic components: a vector database, an embedding model, an LLM, and a framework.
Key Components We'll Use for This RAG Chatbot
This tutorial shows you how to build a simple RAG chatbot in Python using the following components:
- Haystack: An open-source Python framework designed for building production-ready NLP applications, particularly question answering and semantic search systems. Haystack excels at retrieving information from large document collections through its modular architecture that combines retrieval and reader components. Ideal for developers creating search applications, chatbots, and knowledge management systems that require efficient document processing and accurate information extraction from unstructured text.
- Haystack in-memory store: a very simple, in-memory document store with no extra services or dependencies. It is great for experimenting with Haystack, and we do not recommend using it for production. If you want a much more scalable solution for your apps or even enterprise projects, we recommend using Zilliz Cloud, which is a fully managed vector database service built on the open-source Milvusand offers a free tier supporting up to 1 million vectors.)
- Cohere Command R+: A state-of-the-art enterprise-focused LLM optimized for high-efficiency Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and tool use, designed to automate complex workflows. Strengths include multilingual support, scalability, and robust accuracy for enterprise-grade applications. Ideal for automating customer support, data analysis, and knowledge-intensive tasks while ensuring secure, reliable collaboration between AI and human teams.
- OpenAI text-embedding-ada-002: A state-of-the-art embedding model designed to convert text into high-dimensional vectors, capturing semantic meaning for tasks like search, clustering, and recommendations. Renowned for efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, it excels in natural language processing applications, particularly where understanding contextual relationships and similarity across large datasets is critical.
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have a functional chatbot capable of answering questions based on a custom knowledge base.
Note: Since we may use proprietary models in our tutorials, make sure you have the required API key beforehand.
Step 1: Install and Set Up Haystack
import os
import requests
from haystack import Pipeline
from haystack.components.converters import MarkdownToDocument
from haystack.components.preprocessors import DocumentSplitter
from haystack.components.writers import DocumentWriter
Step 2: Install and Set Up Cohere Command R+
To use Cohere models with Haystack for a RAG pipeline, you need to get a Cohere API Key first. You can write this key in:
- The
api_keyinit parameter using Secret API - The
COHERE_API_KEYenvironment variable (recommended)
Now, let's install and set up the Cohere model.
pip install cohere-haystack
from haystack_integrations.components.generators.cohere import CohereGenerator
generator = CohereGenerator(model="command-r-plus")
Step 3: Install and Set Up OpenAI text-embedding-ada-002
Text documents often come with a set of metadata. If they are distinctive and semantically meaningful, you can embed them along with the text of the document to improve retrieval.
from haystack import Document
from haystack.components.embedders import OpenAIDocumentEmbedder
doc = Document(content="some text",meta={"title": "relevant title", "page number": 18})
document_embedder = OpenAIDocumentEmbedder(meta_fields_to_embed=["title"])
docs_w_embeddings = embedder.run(documents=[doc])["documents"]
Now let's install and set up the model.
from haystack import Document
from haystack.components.embedders import OpenAIDocumentEmbedder
from haystack.components.embedders import OpenAITextEmbedder
text_embedder = OpenAITextEmbedder(api_key=Secret.from_token("<your-api-key>"), model="text-embedding-ada-002")
document_embedder = OpenAIDocumentEmbedder(api_key=Secret.from_token("<your-api-key>"), model="text-embedding-ada-002")
Step 4: Install and Set Up Haystack In-memory store
from haystack.document_stores.in_memory import InMemoryDocumentStore
from haystack.components.retrievers import InMemoryEmbeddingRetriever
document_store = InMemoryDocumentStore()
retriever=InMemoryEmbeddingRetriever(document_store=document_store))
Step 5: Build a RAG Chatbot
Now that you’ve set up all components, let’s start to build a simple chatbot. We’ll use the Milvus introduction doc as a private knowledge base. You can replace it your own dataset to customize your RAG chatbot.
url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/milvus-io/milvus-docs/refs/heads/v2.5.x/site/en/about/overview.md'
example_file = 'example_file.md'
response = requests.get(url)
with open(example_file, 'wb') as f:
f.write(response.content)
file_paths = [example_file] # You can replace it with your own file paths.
indexing_pipeline = Pipeline()
indexing_pipeline.add_component("converter", MarkdownToDocument())
indexing_pipeline.add_component("splitter", DocumentSplitter(split_by="sentence", split_length=2))
indexing_pipeline.add_component("embedder", document_embedder)
indexing_pipeline.add_component("writer", DocumentWriter(document_store))
indexing_pipeline.connect("converter", "splitter")
indexing_pipeline.connect("splitter", "embedder")
indexing_pipeline.connect("embedder", "writer")
indexing_pipeline.run({"converter": {"sources": file_paths}})
# print("Number of documents:", document_store.count_documents())
question = "What is Milvus?" # You can replace it with your own question.
retrieval_pipeline = Pipeline()
retrieval_pipeline.add_component("embedder", text_embedder)
retrieval_pipeline.add_component("retriever", retriever)
retrieval_pipeline.connect("embedder", "retriever")
retrieval_results = retrieval_pipeline.run({"embedder": {"text": question}})
# for doc in retrieval_results["retriever"]["documents"]:
# print(doc.content)
# print("-" * 10)
from haystack.utils import Secret
from haystack.components.builders import PromptBuilder
retriever=InMemoryEmbeddingRetriever(document_store=document_store)
text_embedder = OpenAITextEmbedder(api_key=Secret.from_token("<your-api-key>"), model="text-embedding-ada-002")
prompt_template = """Answer the following query based on the provided context. If the context does
not include an answer, reply with 'I don't know'.\n
Query: {{query}}
Documents:
{% for doc in documents %}
{{ doc.content }}
{% endfor %}
Answer:
"""
rag_pipeline = Pipeline()
rag_pipeline.add_component("text_embedder", text_embedder)
rag_pipeline.add_component("retriever", retriever)
rag_pipeline.add_component("prompt_builder", PromptBuilder(template=prompt_template))
rag_pipeline.add_component("generator", generator)
rag_pipeline.connect("text_embedder.embedding", "retriever.query_embedding")
rag_pipeline.connect("retriever.documents", "prompt_builder.documents")
rag_pipeline.connect("prompt_builder", "generator")
results = rag_pipeline.run({"text_embedder": {"text": question}, "prompt_builder": {"query": question},})
print('RAG answer:\n', results["generator"]["replies"][0])
Optimization Tips
As you build your RAG system, optimization is key to ensuring peak performance and efficiency. While setting up the components is an essential first step, fine-tuning each one will help you create a solution that works even better and scales seamlessly. In this section, we’ll share some practical tips for optimizing all these components, giving you the edge to build smarter, faster, and more responsive RAG applications.
Haystack optimization tips
To optimize Haystack in a RAG setup, ensure you use an efficient retriever like FAISS or Milvus for scalable and fast similarity searches. Fine-tune your document store settings, such as indexing strategies and storage backends, to balance speed and accuracy. Use batch processing for embedding generation to reduce latency and optimize API calls. Leverage Haystack's pipeline caching to avoid redundant computations, especially for frequently queried documents. Tune your reader model by selecting a lightweight yet accurate transformer-based model like DistilBERT to speed up response times. Implement query rewriting or filtering techniques to enhance retrieval quality, ensuring the most relevant documents are retrieved for generation. Finally, monitor system performance with Haystack’s built-in evaluation tools to iteratively refine your setup based on real-world query performance.
Haystack in-memory store optimization tips
Haystack in-memory store is just a very simple, in-memory document store with no extra services or dependencies. We recommend that you just experiment it with RAG pipeline within your Haystack framework, and we do not recommend using it for production. If you want a much more scalable solution for your apps or even enterprise projects, we recommend using Zilliz Cloud, which is a fully managed vector database service built on the open-source Milvusand offers a free tier supporting up to 1 million vectors
Cohere Command R+ optimization tips
To optimize Cohere Command R+ in a RAG setup, preprocess input queries by chunking large texts and filtering irrelevant context to reduce noise. Use retrieval-friendly parameters like temperature=0.3 for focused responses and max_tokens=512 to balance detail and conciseness. Fine-tune document retrieval with semantic reranking and metadata filtering to prioritize high-relevance sources. Enable confidence_score to validate output reliability, and cache frequent queries to reduce latency. Monitor token usage and response quality to iteratively adjust retrieval thresholds and generation settings for cost-performance balance.
OpenAI text-embedding-ada-002 optimization tips
To optimize text-embedding-ada-002 in RAG, ensure input text is clean and concise—remove irrelevant content, truncate long documents to the 8191-token limit, and normalize casing/punctuation. Batch embedding requests to reduce latency and costs. Use cosine similarity for relevance scoring, as embeddings are normalized. Cache frequent or static embeddings to avoid reprocessing. Experiment with chunk sizes (256-512 tokens) to balance context retention and granularity. Monitor embedding quality via downstream task performance and adjust preprocessing or retrieval thresholds as needed.
By implementing these tips across your components, you'll be able to enhance the performance and functionality of your RAG system, ensuring it’s optimized for both speed and accuracy. Keep testing, iterating, and refining your setup to stay ahead in the ever-evolving world of AI development.
RAG Cost Calculator: A Free Tool to Calculate Your Cost in Seconds
Estimating the cost of a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline involves analyzing expenses across vector storage, compute resources, and API usage. Key cost drivers include vector database queries, embedding generation, and LLM inference.
RAG Cost Calculator is a free tool that quickly estimates the cost of building a RAG pipeline, including chunking, embedding, vector storage/search, and LLM generation. It also helps you identify cost-saving opportunities and achieve up to 10x cost reduction on vector databases with the serverless option.
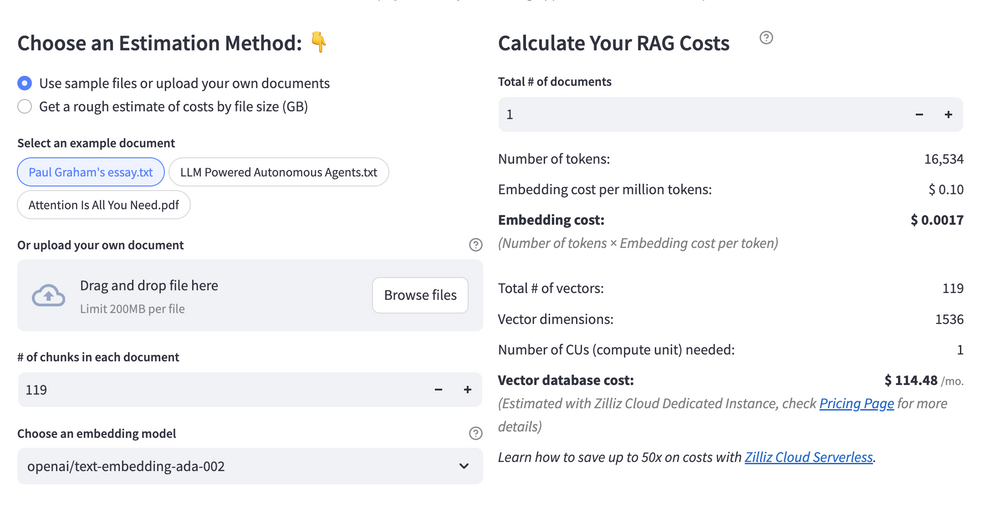 Calculate your RAG cost
Calculate your RAG cost
What Have You Learned?
By now, you’ve unlocked the magic of building a RAG system from scratch! This tutorial walked you through weaving together four powerful tools—Haystack as your framework, Haystack In-memory Store for lightning-fast vector searches, Cohere Command R+ as your brilliant LLM, and OpenAI’s text-embedding-ada-002 to transform text into rich embeddings. You’ve seen how Haystack acts as the backbone, seamlessly connecting your document pipeline to the vector database, where embeddings created by OpenAI’s model turn unstructured data into searchable knowledge. Then, Cohere Command R+ steps in as the brain, synthesizing retrieved context into precise, human-like answers. You’ve learned to orchestrate this symphony: ingesting documents, optimizing retrieval for speed and relevance, and generating responses that feel both informed and natural. It’s like watching a well-oiled machine—each part plays its role, but together, they create something far greater than the sum of their parts!
But it’s not just about making it work—you’ve also picked up pro tips for optimizing your RAG system! Whether adjusting chunk sizes for better context capture, fine-tuning indexing strategies, or leveraging caching to slash costs, you’re now equipped to refine your pipeline for peak performance. And don’t forget that free RAG cost calculator tucked into the tutorial—it’s your secret weapon for balancing efficiency and budget without guesswork. Imagine the possibilities: chatbots that answer like experts, research tools that surface insights in seconds, or creative assistants that spark new ideas. The future of AI-powered applications is in your hands. So go ahead—experiment, tweak, and innovate! Your next breakthrough is just a few lines of code away. Build boldly, optimize fearlessly, and let your RAG creations surprise the world. The tools are here, the knowledge is yours—now go make magic happen!
Further Resources
🌟 In addition to this RAG tutorial, unleash your full potential with these incredible resources to level up your RAG skills.
- How to Build a Multimodal RAG | Documentation
- How to Enhance the Performance of Your RAG Pipeline
- Graph RAG with Milvus | Documentation
- How to Evaluate RAG Applications - Zilliz Learn
- Generative AI Resource Hub | Zilliz
We'd Love to Hear What You Think!
We’d love to hear your thoughts! 🌟 Leave your questions or comments below or join our vibrant Milvus Discord community to share your experiences, ask questions, or connect with thousands of AI enthusiasts. Your journey matters to us!
If you like this tutorial, show your support by giving our Milvus GitHub repo a star ⭐—it means the world to us and inspires us to keep creating! 💖
- Introduction to RAG
- Key Components We'll Use for This RAG Chatbot
- Step 1: Install and Set Up Haystack
- Step 2: Install and Set Up Cohere Command R+
- Step 3: Install and Set Up OpenAI text-embedding-ada-002
- Step 4: Install and Set Up Haystack In-memory store
- Step 5: Build a RAG Chatbot
- Optimization Tips
- RAG Cost Calculator: A Free Tool to Calculate Your Cost in Seconds
- What Have You Learned?
- Further Resources
- We'd Love to Hear What You Think!
Content
Vector Database at Scale
Zilliz Cloud is a fully-managed vector database built for scale, perfect for your RAG apps.
Try Zilliz Cloud for Free