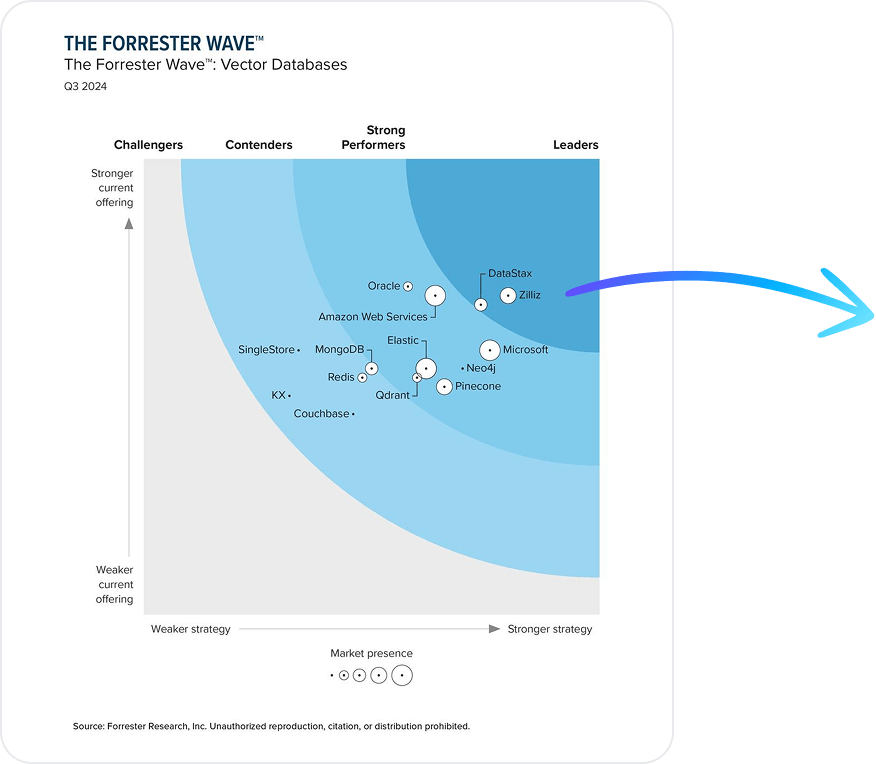
Why 10,000+ Enterprises Teams Switch to Milvus and Zilliz Cloud
Most vector databases look fine in demos or small-scale deployment, but the gaps show up in production—when datasets grow, embeddings refresh frequently, and latency must stay stable under real traffic. That’s where teams turn to Milvus and Zilliz Cloud (managed Milvus service).
Milvus is an open-source, high-performance vector database used by 10,000+ enterprise teams worldwide and trusted by a large open-source community with 43K+ GitHub stars. It handles tens of millions to tens of billions of vectors, frequent inserts and deletes, and hybrid search (vector + keyword + metadata + reranking) without disruptive reindexing or fragile tuning. Performance stays predictable as data volume, query patterns, and model embeddings evolve. This is why Milvus is widely deployed for enterprise RAG, AI agents, semantic and multimodal search, and recommendation systems—workloads where instability becomes visible immediately.
Zilliz Cloud delivers the same Milvus architecture as a managed service, with an advanced vector engine (Cardinal) for higher performance, plus elastic scaling, high availability, enterprise-grade security and compliance, and global deployment. Teams get production-ready reliability without operating or babysitting the database.

“Thanks to the well-designed Python SDK and REST API, we were able to integrate Zilliz Cloud with our LangChain-based architecture in a matter of days. The schema-based collections perfectly aligned with how we structure our data, making the transition nearly seamless."
Nguyễn Ngọc Hải Đăng_ Nguyễn Nhật Khoa
AI Engineer at CX Genie

“Milvus has done an extraordinary job in revolutionizing Likee's video deduplication system, which significantly fueled the growth of BIGO's short-video business."
Xinyang Guo
Software Engineer at BIGO
“You can think of LlamaIndex as a black box around your data and LLM."
Jerry Liu
Co-founder and CEO of LlamaIndex

“We plan to expand the use of Milvus in different fields like content moderation and restriction and customized video services. BIGO and Milvus working together will benefit both businesses and I look forward to Milvus and its community to keep growing and prosper."
Xinyang Guo
Software Engineer at BIGO

“We've gained so much from the Milvus community that we decided to contribute features like "hot reload," which have also benefited our internal operations."
Dennis Zhao
AI Infrastructure Lead at SmartNews

“Milvus consistently outperformed Weaviate, emphasizing the indexing time for scenario S9, closely resembling the FARFETCH product catalog's dimensions."
PEDRO MOREIRA COSTA
Applied Scientist

“Our search system has been much more intelligent, stable, and reliable using Milvus.
"
Rahul Yadav
Software Engineer at Tokopedia

“I can set up Milvus for scale in an hour, not overthinking it, and have a clear architecture path forward to grow my use case much larger without having to redo everything."
Zen Yui
Co-founder & CTO at Troop

“Milvus has dramatically facilitated the MMU team in building various business systems and effectively supports our rapid business growth. Thanks to the Milvus team for developing such a fantastic vector database with stable vector search capabilities and rich functionalities."
The MMU team
Shopee

“When you're engineering a solution as complex as ours, you're not just ticking boxes—you're looking for that sweet spot where all your must-haves intersect. Think of it as an eight-circle Venn diagram; while many databases met one or two of our criteria, Milvus was the only one sitting right at the intersection of all eight. It checked every single box for us—something no other solution managed to do."
Jack Fischer
Co-founder & CTO at Credal AI

“Milvus-powered vector search has been running steadily in our recommendation systems, providing high performance and allowing us more flexibility in selecting models and algorithms."
VIPSHOP Search Service Team
VIPSHOP

“Milvus searches tens of millions of vectors in milliseconds, providing optimal performance while keeping development costs low and resource consumption minimal.
"
Yu Fang
AI scientist at Mozat
“Creating a user-centric interface that's both intuitive and efficient tops our list. We're also immensely proud of the predictive features – like creating comprehensive tools that will tell you how you can save money even after a transaction, along with other tools like customer trip planner already built using your spending transactions and trends. Using vector databases was our first time, and we are very proud of our outcome."
The wellSpent Team
at HackNC
“'wellSpent' is an intuitive mobile application designed to simplify and visualize spending habits. At its core, wellSpent displays a dynamic pie chart that offers a snapshot of expenditures.
Users can access detailed transaction lists and explore predictive features like the travel planner, student debt planner, and other expense planners, all designed to optimize their financial journey. Built on Flutter and powered by Firebase, wellSpent stands as a testament to ensuring every penny is, indeed, well spent."
The wellSpent Team
at HackNC

“When it comes to vector databases, Milvus has impressed us with its performance and scalability, meeting our stringent criteria for handling our AI use case backlog."
Toby Yu
Team Lead of AI, ML, and Platform Solutions

“During batch ingestion tests, Milvus demonstrated that it could complete an entire collection dump into the database at speeds 5-10 times faster than competitors."
Toby Yu
Team Lead of AI, ML, and Platform Solutions
“When we conducted our first test run (on Zilliz Cloud), the performance improvement was astonishing. Our search time went from eight seconds down to sub one second. We were nearly falling off our chairs with amazement at the speed."
Alex Alexander
Co-founder & CEO of Picdmo Inc.

“Zilliz Cloud stood out for us with its comprehensive range of index types, automatically optimizing for the perfect balance between recall and performance. Its robust security and private networking features, combined with the advantage of a fully-managed database, have significantly lightened our operational load, enabling us to concentrate on driving innovation rather than managing backend complexities. "
Ben Kramer
Co-founder & CTO of Monterey AI

“Milvus has not only streamlined but also remarkably expedited the retrieval of millions of semantic vectors, showcasing a nearly tenfold improvement compared to our previous experience with other vector similarity search engines."
Tingting Wang
NLP Algorithm Engineer at Sohu

“I was benchmarking different vector databases, and Milvus was at the top among all the popular options on the market."
Saumil Patel
the Senior Data Scientist from Ivy.ai

“Reliability, scalability, and performance are great. The fact that we can outsource all this kind of administration management and don't have to worry about servers breaking helps us put resources into product development and innovation, which truly differentiates our business. "
Michal Oglodek
CTO of Ivy.ai

“Milvus is renowned as one of the most advanced vector database platforms for AI applications. Rakuten Symphony engineers identified the Milvus Vector Database - an open source database which is horizontally scalable - as their platform of choice for LLM use and developing and maintaining AI applications."
Rakuten Symphony Engineering Team

“When we identify a need for specific data, we can often find the required data in our database the same day using text or image search with Milvus. This greatly improves our data processing efficiency and has a positive effect on our business operations."
Mr. Zhang
BOSCH’s principal software engineer

“We need an indexing technology that can handle complex search requirements and generative models, reduce training costs, improve update efficiency, and adapt flexibly to evolving data and query needs."
Mr. Zhang
BOSCH’s principal software engineer

“Even with numerous concurrent searches, we didn’t notice any slowdown in search speed with Milvus."
Mr. Zhang
BOSCH’s principal software engineer

“Since transitioning from the open-source Milvus vector database to the fully managed Zilliz Cloud, we’ve experienced significant improvements in business performance. We’ve achieved lower operational costs, increased search speed, a more flexible system architecture, and a more stable user experience. Zilliz Cloud also provides expert support to resolve issues quickly and effectively. Overall, Zilliz Cloud has given us greater convenience and a competitive edge, and we are very pleased and optimistic about this change."
Shengyi Pan
CTO of Shulex

“As our business has expanded, the demands on our vector database have increased. We need a solution that minimizes operational costs, offers elastic scaling capabilities to manage vast amounts of vector data and unexpected traffic surges, provides faster vector search speeds, and ensures a high service level agreement (SLA)."
Chenhui Li
Tech Lead at Shulex

“When it comes to vector databases, Milvus has impressed us with its performance and scalability, meeting our stringent criteria for handling our AI use case backlog."
Team Lead
AI, ML, and Platform Solutions

“During batch ingestion tests, Milvus demonstrated that it could complete an entire collection dump into the database at speeds 5–10 times faster than competitors."
Team Lead
AI, ML, and Platform Solutions

“Working with Zilliz Cloud has been transformative for our AI agent architecture. The hybrid search capability alone delivered a 40% accuracy improvement, and the scalability means we never worry about performance, even during the highest traffic periods. It's been essential to our continued growth."
Sasidhar Janaki
Senior Software Engineer at Rexera

“We were facing latency issues and scaling challenges with our previous solutions. When traffic spiked with millions of customer requests, our self-hosted infrastructure couldn't keep up, and document retrieval was taking too long. "
Sasidhar Janaki
Senior Software Engineer at Rexera

“What we wanted was to push intelligence to the user before they even asked. Milvus is what made that viable."
Rob Williams
Co-Founder and CTO at Read AI

“It has saved us cost by at least 25 to 30% on what we were earlier incurring on the vector database, with potential savings reaching up to 40-50% during peak traffic periods. "
Rachit Jindal
Senior AI Engineer at Verbaflo.ai

“The sub-10 millisecond latency for queries is quite the benchmark in the industry for vector databases. Combined with the cost savings and reliability, Zilliz Cloud has become a strategic enabler for our broader vision of transforming conversational AI across industries."
Rachit Jindal
Senior AI Engineer at Verbaflo.ai

“Choosing Zilliz Cloud was one of our best early decisions. It enabled us to build the product we envisioned rather than the product our infrastructure limitations would allow. In AI applications, that difference often determines success or failure."
Ethan Zheng
Co-Founder & CTO of Jobright.ai

“Our strongest competitive moat isn't our AI models—it's our ability to deploy those models at scale with an exceptional user experience. Zilliz Cloud gave us that capability."
Ethan Zheng
Co-Founder & CTO of Jobright.ai

“We were running a multilingual RAG system at scale, indexing all of Wikipedia into tens of millions of high-dimensional vectors. Latency targets were tight. We needed a system that could handle real-time retrieval over millions of knowledge vectors without breaking under load. Zilliz gave us that. It freed up engineering cycles and let us focus on improving reasoning on the model side, not managing infrastructure. That reliability mattered because we were operating at 3,500+ dimensions per vector, across a fast-growing corpus, with sub-300ms latency requirements in production.
"
Dr. Pratyush Kumar
Co-Founder of Sarvam

“Zilliz Cloud gave us the speed and scale we needed to power visual search at Leboncoin, meeting our sub-200ms latency target and making product discovery seamless for millions of users."
Yann Lemonnier
ML Engineer

“With Zilliz Cloud, we moved from operating at our limits to building with confidence. It gave us the scale, performance, and flexibility to protect music rights in real time—something we couldn’t achieve with traditional systems."
George Kastrinakis
Director of Data Science and AI Services at Orfium

“It was the best thing to offer—performance-wise, cost-wise, and ease-of-use-wise."
George Kastrinakis
Director of Data Science and AI Services at Orfium

“Milvus transformed our ability to detect semantic plagiarism at scale. We can now process variable workloads ranging from 10 to 10,000+ documents daily while maintaining cost-effectiveness, which would have been impossible with traditional solutions."
Teis Petersen
Engineering Team Lead, UNIwise

“If I were to choose again, I would still choose Milvus at this point. The scalability, documentation quality, and continuous innovation make it the right foundation for our plagiarism detection platform."
Teis Petersen
Engineering Team Lead, UNIwise

“Milvus has become the bridge that connects our multi-modal foundation models with real-world applications. It's not just about performance – it's about enabling entirely new approaches to biological discovery that were previously impossible."
Xiaoming Zhang
VP of Technology at Biomap

“Milvus has become the only technical choice for vector databases in our upcoming business expansion across the life sciences industry."
Xiaoming Zhang
VP of Technology at Biomap

“Among Milvus's rich vector search capabilities, features such as support for multiple ANN index types, multi-vector support, and hybrid search have proven especially valuable in real-world service environments. As Milvus continues to evolve with new capabilities, NAVER expects even broader applications across its services."
NAVER Engineering Team
“Milvus’s real advantage was how easy and friendly it made things to understand and execute."
Hanlian Lyu
a Product Owner and BI Expert at Volvo Cars

“Whenever we demonstrate our solution with Milvus, we’re effectively crushing the cloud vendor solution’s performance. It’s a great benchmark because most enterprise users already know the vendor solution, so the comparison is immediate."
Hanlian Lyu
a Product Owner and BI Expert at Volvo Cars

“From a system stability perspective, it's really quite good. Over the year-plus that we've been using it—from version 2.4.3 to now 2.5.8—I honestly haven't encountered many issues. The system can just run there for months, with new data being written every day and users searching every day, without any problems. I don't need to worry about it."
Jianping Wang
NVIDIA engineer

“We tested every mainstream vector database, and Milvus delivered the best overall performance."
Su Wei
CTO of Shining

“From a system stability perspective, it's really quite good. Over the year-plus that we've been using it—from version 2.4.3 to now 2.5.8—I honestly haven't encountered many issues. The system can just run there for months, with new data being written every day and users searching every day, without any problems. I don't need to worry about it."
Team Lead
Senior Infrastructure Engineer

“From a performance standpoint, Zilliz Cloud's retrieval speed far exceeds our existing system. We achieved approximately 70% reduction in retrieval latency, which translates to a 4-5x improvement in overall problem-solving time when we successfully match original questions. Whether measured by speed, cost, or overall value, Zilliz Cloud perfectly met our expectations."
Dr. Nick Yuan
CTO

“The migration was incredibly smooth. Using the built-in tools, we were able to import our data from Pinecone with essentially one click. The technical support has also been excellent — our questions get resolved almost instantly, and the documentation, demos, and examples are thorough and easy to work with."
Technical Team

“We don’t have any concern related to database operations anymore after adopting Zilliz Cloud. Before, we had a lot of troubles—memory suddenly wasn’t enough, we needed to scale up, we didn’t have auto-scaling. All of those things caused a lot of problems. The most obvious benefits for us are the management and the data ingestion. That’s very attractive."
Lixiang Li
the engineering team lead at JERA

“Milvus delivers unparalleled performance and flexibility, integrating seamlessly with leading vector index libraries like Faiss. Its intuitive API and robust solutions for high availability make it an indispensable tool in our APK security efforts."
Wei Huang
Senior Research Engineer

“Zilliz Cloud perfectly aligns with MindStudio's vision. Its high-performance, secure platform and multi-tenancy simplifies data management and unlocks unprecedented productivity and innovation for our users’ AI applications. "
Sean Thielen
CTO @ MindStudio

“I appreciated using the open standard evaluation benchmarks for machine learning in general; this is also true for vector databases. The ones that Zilliz often publicizes have been beneficial, and the fact that they are open is significant. "
Sam Butler
Director of Machine Learning @ Dopple.AI

“Zilliz Cloud enabled us to scale search while dramatically reducing our costs. Its hybrid search capabilities helped us achieve higher relevance for both text and image queries."
Celine Lightfoot
CTO of Beni

“I really like how Milvus' hybrid search allowed me to blend semantic and keyword search, which is crucial in a domain as technical and complex as EU policy."
Alessandro Saccoia
Co-Founder @ Veridien.ai

“The competitive advantage for meeting transcription products in the future will come from personalization – providing tailored insights and recommendations based on each user's specific meeting data and usage patterns. This is why performant vector search is imperative."
TJ Dai
CTO of Notta

“Zilliz is a very integral part of our workflow. If we just swapped Zilliz Cloud with something else, the kind of loops that we get might not make sense, which means the end composition might not sound very nice or might not be very accurate to the text prompt you had given."
Sangarshanan Veera
Senior Software Engineer at Beatoven.ai

“We have the full end-to-end data... law as a timeline. We have the incident, the start, everything that's happening, and the conclusion of the case. There's an enormous amount of power in having that all within the work system."
Brianna Connelly
AI Team Lead at Filevine

“As a client of a law firm, at some point clients will demand that their law firms use AI because it's going to make them a better attorney to have the curation done versus some of the practices now where they just don't have complete info."
Brianna Connelly
AI Team Lead at Filevine

“We have achieved a true consciousness of data... bringing the data together in the way that an individual doing their job needs to see it."
Nathan Morris
Co-Founder of Filevine

“We've got millions of monthly active users and all of the underlying data when we're trying to go find related conversations, find updates to an action item, find referenced documents...Milvus serves as the central repository and powers our information retrieval among billions of records."
Rob Williams
Co-Founder and CTO at Read AI

“Milvus scaled really well with batches ranging from 1,000 to millions of records. That really impressed me."
Todor Voynikov
Data Engineer at TrialHub

“After integrating Zilliz Cloud vector database service, our system performance has significantly improved. During implementation, the Zilliz Cloud expert team provided excellent support and assistance, giving our EviMed platform a strong competitive advantage in the industry."
Dr. Zeyuan Wang
CEO of EviMed

“With Zilliz Cloud, we've achieved query latencies as low as 5-10ms across our million-vector database. This represents performance that's twice as fast as our previous solution, which directly translates to more responsive chatbots for our customers."
Nguyễn Ngọc Hải Đăng_ Nguyễn Nhật Khoa
AI Engineer at CX Genie

“By migrating to Zilliz Cloud, we've reduced our vector database infrastructure costs by approximately 70% compared to our self-hosted setup. This allows us to reinvest those savings into improving our core AI capabilities rather than managing database infrastructure."
Nguyễn Ngọc Hải Đăng_ Nguyễn Nhật Khoa
AI Engineer at CX Genie

“Thanks to the well-designed Python SDK and REST API, we were able to integrate Zilliz Cloud with our LangChain-based architecture in a matter of days. The schema-based collections perfectly aligned with how we structure our data, making the transition nearly seamless."
Nguyễn Ngọc Hải Đăng_ Nguyễn Nhật Khoa
AI Engineer at CX Genie

“Milvus has done an extraordinary job in revolutionizing Likee's video deduplication system, which significantly fueled the growth of BIGO's short-video business."
Xinyang Guo
Software Engineer at BIGO