How to Install and Run OpenClaw (Previously Clawdbot/Moltbot) on Mac

OpenClaw is an open-source, self-hosted gateway that bridges your everyday messaging apps to AI coding agents. Instead of switching between tabs, apps, and interfaces, you send a message from WhatsApp or Telegram and get an AI-powered response right in your pocket. It's MIT licensed, runs on your hardware, and keeps you in full control of your data.
In this tutorial, we'll walk through everything you need to install and run OpenClaw on macOS — from prerequisites to your first working chat.
What You'll Need
Before you begin, make sure you have the following:
- macOS (any recent version)
- Node.js 22 or newer — the installer script will handle this for you if it's not already installed, but it's good to check
- An API key — Anthropic is recommended by the OpenClaw team
- About 5 minutes of your time
To check your current Node version, open Terminal and run:
node --version
If you see v22.x.x or higher, you're good to go. If not, don't worry — the installer will take care of it.
Step 1: Install OpenClaw via the Installer Script (Recommended)
The fastest way to install OpenClaw on macOS is the one-line installer script. It handles Node detection, CLI installation, and launches the onboarding wizard — all in one step.
Open Terminal and run:
curl -fsSL https://openclaw.ai/install.sh | bash
That's it. The script will download the CLI, install it globally via npm, and kick off the onboarding wizard automatically.
Alternative: Install via npm Directly
If you already have Node 22+ and prefer manual control, you can install OpenClaw with npm:
npm install -g openclaw@latest
openclaw onboard --install-daemon
Alternative: Install via pnpm
If pnpm is your package manager of choice:
pnpm add -g openclaw@latest
pnpm approve-builds -g # approve openclaw, node-llama-cpp, sharp, etc.
openclaw onboard --install-daemon
Note: pnpm requires explicit approval for packages with build scripts. After the first install shows the "Ignored build scripts" warning, run pnpm approve-builds -g and select the listed packages.
Troubleshooting: sharp Build Errors
If you have libvips installed globally (common on macOS via Homebrew) and sharp fails during installation, force prebuilt binaries:
SHARP_IGNORE_GLOBAL_LIBVIPS=1 npm install -g openclaw@latest
If you see the error sharp: Please add node-gyp to your dependencies, either install build tooling (Xcode Command Line Tools + npm install -g node-gyp) or use the environment variable above.
Step 2: Run the Onboarding Wizard
If the installer script didn't automatically launch it, start the onboarding wizard manually:
openclaw onboard --install-daemon
The wizard walks you through configuring auth, gateway settings, and optional channel connections. It also installs OpenClaw as a background service (daemon), so the Gateway stays running even after you close Terminal.
What the Wizard Configures
- Authentication — generates a token for the Gateway so local and remote clients must authenticate
- Gateway settings — port, bind address, and service installation
- Channel connections — optional setup for WhatsApp, Telegram, Discord, and more
Step 3: Verify the Gateway Is Running
Once onboarding completes, check that the Gateway is up:
openclaw gateway status
You should see confirmation that the Gateway is running. If you want to run it in the foreground for debugging or quick testing, use:
openclaw gateway --port 18789
For a full health check:
openclaw health
Step 4: Open the Control UI (Dashboard)
The fastest way to start chatting with OpenClaw is through the browser-based Control UI — no channel setup required.
Run:
openclaw dashboard
This copies the dashboard URL, opens your browser if possible, and displays the link. By default, the Control UI is served at:
http://127.0.0.1:18789/
If the dashboard prompts for authentication, paste the token from your Gateway config. You can retrieve it with:
openclaw config get gateway.auth.token
Security note: The Control UI is an admin surface — it provides access to chat, configuration, and execution approvals. Do not expose it publicly. Stick to localhost, Tailscale Serve, or an SSH tunnel.
Step 5: Connect a Chat Channel (Optional)
While the Control UI gives you instant access to chat, the real power of OpenClaw is messaging your AI agent from the apps you already use. Here's a quick overview of supported channels:
| Channel | Setup Complexity | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Telegram | Easiest | Simple bot token |
| Easy | QR pairing required; stores more state on disk | |
| Discord | Moderate | Bot API + Gateway |
| iMessage | Moderate | Recommended via BlueBubbles macOS server |
| IRC | Low | Classic IRC; channels + DMs |
| Slack | Moderate | Bolt SDK; workspace apps |
| Signal | Moderate | Privacy-focused; uses signal-cli |
Multiple channels can run simultaneously — configure as many as you want and OpenClaw routes messages per chat.
Check out this post for: OpenClaw Tutorial: Connect to Slack for Local AI Assistant - Milvus Blog
Quick Example: Pair WhatsApp
To connect WhatsApp, run:
openclaw channels login
Follow the QR pairing flow, and you'll be able to message your AI agent directly from WhatsApp.
Step 6: Send a Test Message
With a channel configured, send a test message from the CLI:
openclaw message send --target +15555550123 --message "Hello from OpenClaw"
Replace the phone number with your own. If everything is wired correctly, you'll see the message arrive in your messaging app — and OpenClaw's AI agent will respond.
Optional: Build from Source
For contributors or anyone who wants to run from a local checkout:
git clone https://github.com/openclaw/openclaw.git
cd openclaw
pnpm install
pnpm ui:build
pnpm build
Link the CLI globally:
pnpm link --global
Then run onboarding:
openclaw onboard --install-daemon
For hot-reload during development, use pnpm gateway:watch instead of the standard gateway command.
Optional: macOS App Onboarding
OpenClaw also offers a native macOS app (menu bar) with its own onboarding flow. If you're using the app:
- Approve the macOS security warning when first launching
- Allow "Find Local Networks" permission
- Choose Local vs. Remote — select "This Mac" for a local-only Gateway
- Grant permissions — the app may request Automation, Notifications, Accessibility, and other TCC permissions depending on your use case
- Install the CLI (optional) — the app can install the global
openclawCLI via npm so terminal workflows work alongside the app - Chat in the onboarding session — the app opens a dedicated chat so the agent can introduce itself
The stable workflow recommended by the OpenClaw docs: install and launch OpenClaw.app, complete the onboarding checklist, then link your channels with openclaw channels login.
Configuration Basics
OpenClaw stores its configuration at ~/.openclaw/openclaw.json. Out of the box, it uses the bundled Pi binary in RPC mode with per-sender sessions — no configuration needed.
If you want to restrict who can message your agent, add an allowFrom rule:
{
"channels": {
"whatsapp": {
"allowFrom": ["+15555550123"],
"groups": {
"*": {
"requireMention": true
}
}
}
},
"messages": {
"groupChat": {
"mentionPatterns": ["@openclaw"]
}
}
}
Key File Locations on macOS
| Path | Purpose |
|---|---|
~/.openclaw/openclaw.json | Main configuration file |
~/.openclaw/workspace/ | Skills, prompts, memories |
~/.openclaw/credentials/ | Channel credentials |
~/.openclaw/agents/<agentId>/sessions/ | Agent session data |
/tmp/openclaw/ | Logs |
Useful Environment Variables
| Variable | Purpose |
|---|---|
OPENCLAW_HOME | Override home directory for internal path resolution |
OPENCLAW_STATE_DIR | Override the state directory |
OPENCLAW_CONFIG_PATH | Override the config file path |
Troubleshooting: openclaw Not Found
If your shell can't find the openclaw command after installation, the issue is almost always a missing PATH entry.
Quick diagnosis:
node -v
npm -v
npm prefix -g
echo "$PATH"
If the output of npm prefix -g plus /bin isn't in your $PATH, add it to your shell startup file (~/.zshrc for modern macOS):
export PATH="$(npm prefix -g)/bin:$PATH"
Then open a new Terminal window or run source ~/.zshrc.
Troubleshooting: "Unauthorized" / 1008 Error in Dashboard
If the Control UI shows an unauthorized error:
- Make sure the Gateway is reachable:
openclaw status - Retrieve the token:
openclaw config get gateway.auth.token - In the dashboard settings, paste the token into the auth field and reconnect
If you need to generate a fresh token:
openclaw doctor --generate-gateway-token
What You Now Have
After completing this tutorial, you have:
- A running Gateway on your Mac
- Authentication configured for secure access
- Control UI access for browser-based chat
- Optionally, one or more connected messaging channels (WhatsApp, Telegram, Discord, etc.)
From here, you can explore multi-agent routing, workspace isolation, media support, and the full range of OpenClaw's capabilities.
Resources
- What You'll Need
- Step 1: Install OpenClaw via the Installer Script (Recommended)
- Step 2: Run the Onboarding Wizard
- Step 3: Verify the Gateway Is Running
- Step 4: Open the Control UI (Dashboard)
- Step 5: Connect a Chat Channel (Optional)
- Step 6: Send a Test Message
- Optional: Build from Source
- Optional: macOS App Onboarding
- Configuration Basics
- Troubleshooting: `openclaw` Not Found
- Troubleshooting: "Unauthorized" / 1008 Error in Dashboard
- What You Now Have
- Resources
Content
Start Free, Scale Easily
Try the fully-managed vector database built for your GenAI applications.
Try Zilliz Cloud for FreeKeep Reading
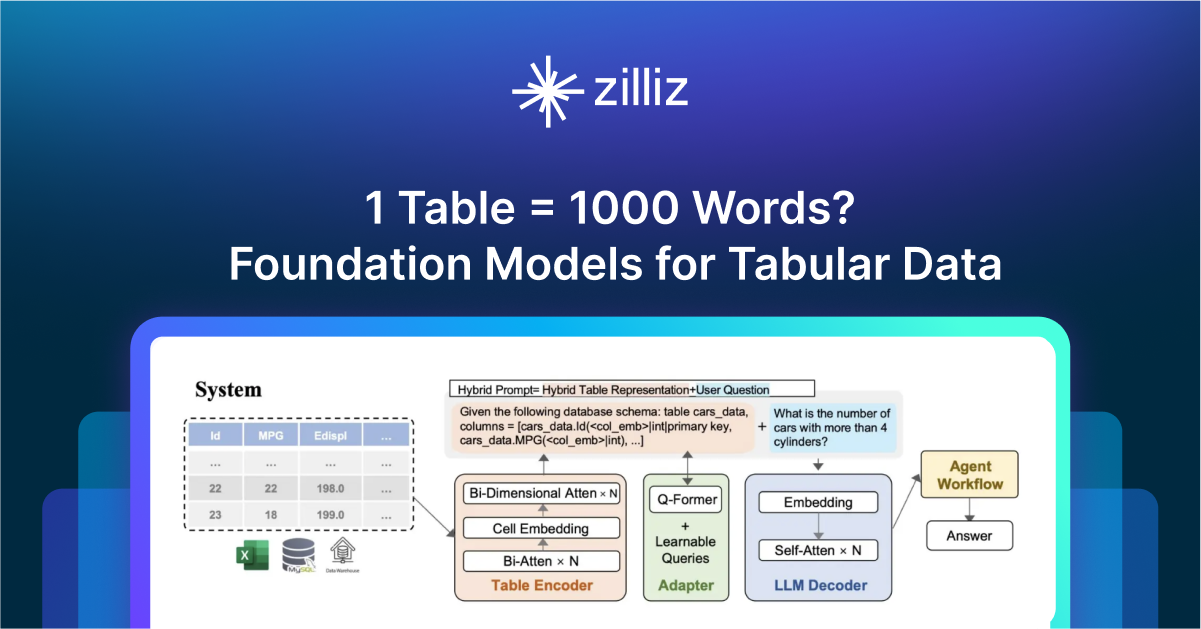
1 Table = 1000 Words? Foundation Models for Tabular Data
TableGPT2 automates tabular data insights, overcoming schema variability, while Milvus accelerates vector search for efficient, scalable decision-making.

Vector Databases vs. Document Databases
Use a vector database for similarity search and AI-powered applications; use a document database for flexible schema and JSON-like data storage.

AI Integration in Video Surveillance Tools: Transforming the Industry with Vector Databases
Discover how AI and vector databases are revolutionizing video surveillance with real-time analysis, faster threat detection, and intelligent search capabilities for enhanced security.
