Build RAG Chatbot with Llamaindex, Faiss, Gemini 1.5 Pro, and jina-colbert-v2
Introduction to RAG
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a game-changer for GenAI applications, especially in conversational AI. It combines the power of pre-trained large language models (LLMs) like OpenAI’s GPT with external knowledge sources stored in vector databases such as Milvus and Zilliz Cloud, allowing for more accurate, contextually relevant, and up-to-date response generation. A RAG pipeline usually consists of four basic components: a vector database, an embedding model, an LLM, and a framework.
Key Components We'll Use for This RAG Chatbot
This tutorial shows you how to build a simple RAG chatbot in Python using the following components:
- Llamaindex: a data framework that connects large language models (LLMs) with various data sources, enabling efficient retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). It helps structure, index, and query private or external data, optimizing LLM applications for search, chatbots, and analytics.
- Faiss: also known as Facebook AI Similarity Search, is an open-source vector search library that allows developers to quickly search for semantically similar multimedia data within a massive dataset of unstructured data. (If you want a much more scalable solution or hate to manage your own infrastructure, we recommend using Zilliz Cloud, which is a fully managed vector database service built on the open-source Milvus and offers a free tier supporting up to 1 million vectors.)
- Gemini 1.5 Pro: A highly capable AI model designed for advanced reasoning, contextual understanding, and in-depth text generation. Well-suited for research, enterprise knowledge management, and sophisticated AI applications requiring accurate, multi-turn dialogue and deep contextual comprehension.
- Jina-ColBERT-v2: A dense passage retrieval model optimized for semantic search and document ranking. It combines ColBERT's contextualized late interaction with efficient indexing, delivering high accuracy in understanding query intent and matching relevant text. Ideal for large-scale enterprise search, Q&A systems, and content discovery platforms requiring nuanced semantic understanding and rapid retrieval.
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have a functional chatbot capable of answering questions based on a custom knowledge base.
Note: Since we may use proprietary models in our tutorials, make sure you have the required API key beforehand.
Step 1: Install and Set Up Llamaindex
pip install llama-index
Step 2: Install and Set Up Gemini 1.5 Pro
%pip install llama-index-llms-google-genai llama-index
from llama_index.llms.google_genai import GoogleGenAI
llm = GoogleGenAI(
model="gemini-1.5-pro",
# api_key="some key", # uses GOOGLE_API_KEY env var by default
)
Step 3: Install and Set Up jina-colbert-v2
%pip install llama-index-embeddings-jinaai
You may also need other packages that do not come direcly with llama-index.
!pip install Pillow
from llama_index.embeddings.jinaai import JinaEmbedding
embed_model = JinaEmbedding(
api_key=jinaai_api_key,
model="jina-colbert-v2",
# choose `retrieval.passage` to get passage embeddings
task="retrieval.passage",
)
Step 4: Install and Set Up Faiss
%pip install llama-index-vector-stores-faiss
from llama_index.core import (
SimpleDirectoryReader,
load_index_from_storage,
VectorStoreIndex,
StorageContext,
)
from llama_index.vector_stores.faiss import FaissVectorStore
vector_store = FaissVectorStore(faiss_index=faiss_index)
Step 5: Build a RAG Chatbot
Now that you’ve set up all components, let’s start to build a simple chatbot. We’ll use the Milvus introduction doc as a private knowledge base. You can replace it with your own dataset to customize your RAG chatbot.
import requests
from llama_index.core import SimpleDirectoryReader
# load documents
url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/milvus-io/milvus-docs/refs/heads/v2.5.x/site/en/about/overview.md'
example_file = 'example_file.md' # You can replace it with your own file paths.
response = requests.get(url)
with open(example_file, 'wb') as f:
f.write(response.content)
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader(
input_files=[example_file]
).load_data()
print("Document ID:", documents[0].doc_id)
storage_context = StorageContext.from_defaults(vector_store=vector_store)
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(
documents, storage_context=storage_context, embed_model=embed_model
)
query_engine = index.as_query_engine(llm=llm)
res = query_engine.query("What is Milvus?") # You can replace it with your own question.
print(res)
Example output
Milvus is a high-performance, highly scalable vector database designed to operate efficiently across various environments, from personal laptops to large-scale distributed systems. It is available as both open-source software and a cloud service. Milvus excels in managing unstructured data by converting it into numerical vectors through embeddings, which facilitates fast and scalable searches and analytics. The database supports a wide range of data types and offers robust data modeling capabilities, allowing users to organize their data effectively. Additionally, Milvus provides multiple deployment options, including a lightweight version for quick prototyping and a distributed version for handling massive data scales.
Optimization Tips
As you build your RAG system, optimization is key to ensuring peak performance and efficiency. While setting up the components is an essential first step, fine-tuning each one will help you create a solution that works even better and scales seamlessly. In this section, we’ll share some practical tips for optimizing all these components, giving you the edge to build smarter, faster, and more responsive RAG applications.
LlamaIndex optimization tips
To optimize LlamaIndex for a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) setup, structure your data efficiently using hierarchical indices like tree-based or keyword-table indices for faster retrieval. Use embeddings that align with your use case to improve search relevance. Fine-tune chunk sizes to balance context length and retrieval precision. Enable caching for frequently accessed queries to enhance performance. Optimize metadata filtering to reduce unnecessary search space and improve speed. If using vector databases, ensure indexing strategies align with your query patterns. Implement async processing to handle large-scale document ingestion efficiently. Regularly monitor query performance and adjust indexing parameters as needed for optimal results.
Faiss Optimization Tips
To enhance the performance of the Faiss library in a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system, begin by selecting the appropriate index type based on your data volume and query speed requirements; for example, using an IVF (Inverted File) index can significantly speed up queries on large datasets by reducing the search space. Optimize your indexing process by using the nlist parameter to partition data into smaller clusters and set an appropriate number of probes (nprobe) during retrieval to balance between speed and accuracy. Ensure the vectors are properly normalized and consider using 16-bit or 8-bit quantization during indexing to reduce memory footprints for large datasets while maintaining reasonable retrieval accuracy. Additionally, consider leveraging GPU acceleration if available, as Faiss highly benefits from parallel processing, leading to faster nearest neighbor searches. Continuous fine-tuning and benchmarking with varying parameters and configurations can guide you in finding the most efficient setup specific to your data characteristics and retrieval requirements.
Gemini 1.5 Pro optimization tips
Gemini 1.5 Pro benefits from structured and high-quality retrieval in a RAG pipeline. Optimize by ensuring vector search returns highly relevant documents using fine-tuned embeddings. Use adaptive chunking strategies based on query complexity to control token usage effectively. Implement document reranking techniques to improve result relevance. Leverage structured prompting to guide the model’s reasoning. Monitor latency and retrieval efficiency to refine your pipeline continuously.
jina-colbert-v2 optimization tips
To optimize jina-colbert-v2 in a RAG setup, ensure input text is preprocessed by truncating or chunking documents to fit its 512-token limit, preserving context. Use batch inference for dense embeddings to maximize GPU utilization. Fine-tune on domain-specific data to improve relevance. Leverage ColBERT’s late interaction by precomputing document embeddings and caching them for faster retrieval. Adjust the compression ratio for query-document token tensors to balance speed and accuracy. Filter irrelevant documents early using metadata to reduce computational overhead. Monitor retrieval latency and accuracy to iteratively refine parameters.
By implementing these tips across your components, you'll be able to enhance the performance and functionality of your RAG system, ensuring it’s optimized for both speed and accuracy. Keep testing, iterating, and refining your setup to stay ahead in the ever-evolving world of AI development.
RAG Cost Calculator: A Free Tool to Calculate Your Cost in Seconds
Estimating the cost of a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline involves analyzing expenses across vector storage, compute resources, and API usage. Key cost drivers include vector database queries, embedding generation, and LLM inference.
RAG Cost Calculator is a free tool that quickly estimates the cost of building a RAG pipeline, including chunking, embedding, vector storage/search, and LLM generation. It also helps you identify cost-saving opportunities and achieve up to 10x cost reduction on vector databases with the serverless option.
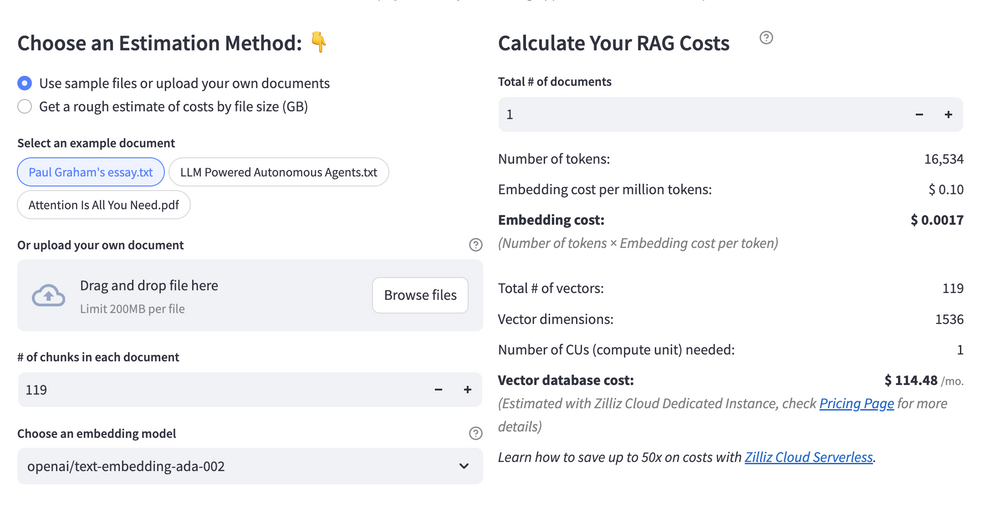 Calculate your RAG cost
Calculate your RAG cost
What Have You Learned?
Congratulations on making it through this tutorial! You’ve taken a fantastic leap toward mastering the art of building a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system by integrating some of the most powerful components in the field. We explored how LlamaIndex provides a solid framework that allows you to manage and connect various data sources effortlessly. Then, harnessing the capabilities of the Faiss vector database means you can perform lightning-fast similarity searches, unlocking the potential to retrieve relevant information when it matters most. And let's not forget about the immense power of Gemini 1.5 Pro: it’s your key to dynamically generate high-quality content based on the context you provide! Lastly, the jina-colbert-v2 embedding model ensures that your RAG system understands nuanced semantic meanings in data, resulting in richer and more informative responses.
Along the way, we shared some handy optimization tips to fine-tune your system for exceptional performance and introduced a free RAG cost calculator to help you estimate your project’s viability. It’s exciting to think about the innovative applications you can create with these tools! Now that you’ve built a robust foundation, it’s time to roll up your sleeves and start exploring the endless possibilities of your own RAG applications. Get hands-on, experiment, and let your creativity flourish. The world is waiting for your innovations—go out there and make an impact!
Further Resources
🌟 In addition to this RAG tutorial, unleash your full potential with these incredible resources to level up your RAG skills.
- How to Build a Multimodal RAG | Documentation
- How to Enhance the Performance of Your RAG Pipeline
- Graph RAG with Milvus | Documentation
- How to Evaluate RAG Applications - Zilliz Learn
- Generative AI Resource Hub | Zilliz
We'd Love to Hear What You Think!
We’d love to hear your thoughts! 🌟 Leave your questions or comments below or join our vibrant Milvus Discord community to share your experiences, ask questions, or connect with thousands of AI enthusiasts. Your journey matters to us!
If you like this tutorial, show your support by giving our Milvus GitHub repo a star ⭐—it means the world to us and inspires us to keep creating! 💖
- Introduction to RAG
- Key Components We'll Use for This RAG Chatbot
- Step 1: Install and Set Up Llamaindex
- Step 2: Install and Set Up Gemini 1.5 Pro
- Step 3: Install and Set Up jina-colbert-v2
- Step 4: Install and Set Up Faiss
- Step 5: Build a RAG Chatbot
- Optimization Tips
- RAG Cost Calculator: A Free Tool to Calculate Your Cost in Seconds
- What Have You Learned?
- Further Resources
- We'd Love to Hear What You Think!
Content
Vector Database at Scale
Zilliz Cloud is a fully-managed vector database built for scale, perfect for your RAG apps.
Try Zilliz Cloud for FreeKeep Reading

Finding the Right Fit: Embedding Creation for AI Retrieval (RAG) in Zilliz Cloud Pipelines from OSS, VoyageAI, and OpenAI

Crafting Superior RAG for Code-Intensive Texts with Zilliz Cloud Pipelines and Voyage AI

Do We Still Need Vector Databases for RAG with OpenAI's Releasing of Its Built-In Retrieval?
