Building an Intelligent QA System with NLP and Milvus
Milvus Project:github.com/milvus-io/milvus
The question answering system is commonly used in the field of natural language processing. It is used to answer questions in the form of natural language and has a wide range of applications. Typical applications include: intelligent voice interaction, online customer service, knowledge acquisition, personalized emotional chatting, and more. Most question answering systems can be classified as: generative and retrieval question answering systems, single-round question answering and multi-round question answering systems, open question answering systems, and specific question answering systems.
This article mainly deals with a QA system designed for a specific field, which is usually called an intelligent customer service robot. In the past, building a customer service robot usually required conversion of the domain knowledge into a series of rules and knowledge graphs. The construction process relies heavily on “human” intelligence. Once the scenes were changed, a lot of repetitive work would be required. With the application of deep learning in natural language processing (NLP), machine reading can automatically find answers to matching questions directly from documents. The deep learning language model converts the questions and documents to semantic vectors to find the matching answer.
This article uses Google’s open source BERT model and Milvus, an open source vector search engine, to quickly build a Q&A bot based on semantic understanding.
Overall Architecture
This article implements a question answering system through semantic similarity matching. The general construction process is as follows:
- Obtain a large number of questions with answers in a specific field ( a standard question set).
- Use the BERT model to convert these questions into feature vectors and store them in Milvus. And Milvus will assign a vector ID to each feature vector at the same time.
- Store these representative question IDs and their corresponding answers in PostgreSQL.
When a user asks a question:
- The BERT model converts it to a feature vector.
- Milvus performs a similarity search and retrieves the ID most similar to the question.
- PostgreSQL returns the corresponding answer.
The system architecture diagram is as follows (the blue lines represent the import process and the yellow lines represent the query process):
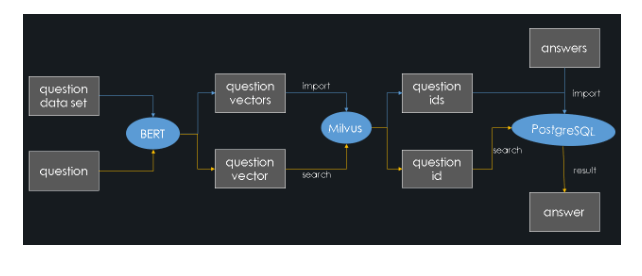 Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Next, we will show you how to build an online Q&A system step by step.
Steps to Build the Q&A System
Before you start, you need to install Milvus and PostgreSQL. For the specific installation steps, see the Milvus official website.
1. Data preparation
The experimental data in this article comes from: https://github.com/chatopera/insuranceqa-corpus-zh
The data set contains question and answer data pairs related to the insurance industry. In this article we extracts 20,000 question and answer pairs from it. Through this set of question and answer data sets, you can quickly build a customer service robot for the insurance industry.
2. Generate feature vectors
This system uses a model that BERT has pre-trained. Download it from the link below before starting a service: https://storage.googleapis.com/bert_models/2018_10_18/cased_L-24_H-1024_A-16.zip
Use this model to convert the question database to feature vectors for future similarity search. For more information about the BERT service, see https://github.com/hanxiao/bert-as-service.
 Figure 2.
Figure 2.
3. Import to Milvus and PostgreSQL
Normalize and import the generated feature vectors import to Milvus, and then import the IDs returned by Milvus and the corresponding answers to PostgreSQL. The following shows the table structure in PostgreSQL:
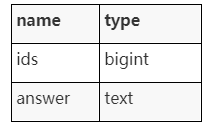 Figure 3.
Figure 3.
 Figure 4.
Figure 4.
4. Retrieve Answers
The user inputs a question, and after generating the feature vector through BERT, they can find the most similar question in the Milvus library. This article uses the cosine distance to represent the similarity between two sentences. Because all vectors are normalized, the closer the cosine distance of the two feature vectors to 1, the higher the similarity.
In practice, your system may not have perfectly matched questions in the library. Then, you can set a threshold of 0.9. If the greatest similarity distance retrieved is less than this threshold, the system will prompt that it does not include related questions.
 Figure 5.
Figure 5.
System Demonstration
The following shows an example interface of the system:
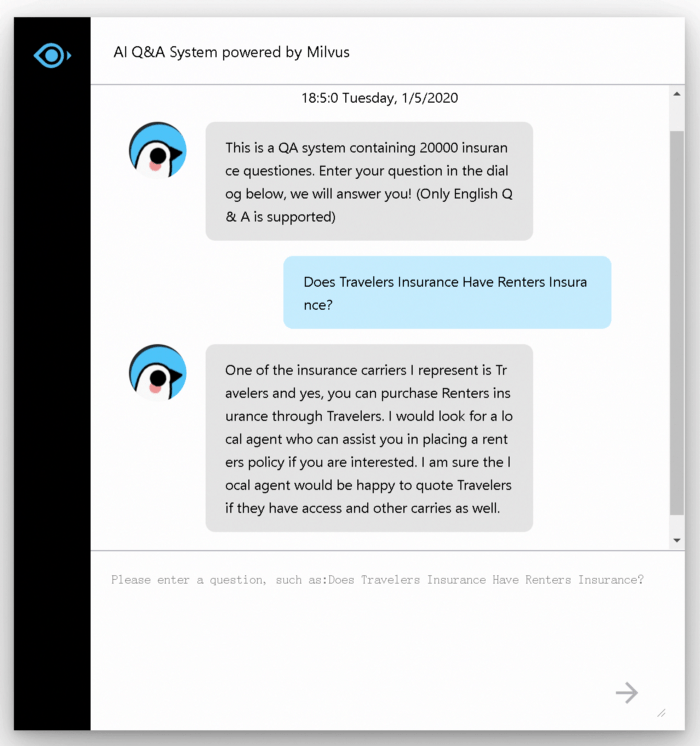 Figure 6.
Figure 6.
Enter your question in the dialog box and you will receive a corresponding answer:
 Figure 7.
Figure 7.
Summary
After reading this article, we hope you find it easy to build your own Q&A System.
With the BERT model, you no longer need to sort and organize the text corpora beforehand. At the same time, thanks to the high performance and high scalability of the open source vector search engine Milvus, your QA system can support a corpus of up to hundreds of millions of texts.
Milvus has officially joined the Linux AI (LF AI) Foundation for incubation. You are welcome to join the Milvus community and work with us to accelerate the application of AI technologies!
=> Try our online demo here: https://www.milvus.io/scenarios
Start Free, Scale Easily
Try the fully-managed vector database built for your GenAI applications.
Try Zilliz Cloud for FreeKeep Reading

Milvus 2.6.x Now Generally Available on Zilliz Cloud, Making Vector Search Faster, Smarter, and More Cost-Efficient for Production AI
Milvus 2.6.x is now GA on Zilliz Cloud, delivering faster vector search, smarter hybrid queries, and lower costs for production RAG and AI applications.

The Real Bottlenecks in Autonomous Driving — And How AI Infrastructure Can Solve Them
Autonomous driving is data-bound. Vector databases unlock deep insights from massive AV data, slashing costs and accelerating edge-case discovery.

How to Build RAG with Milvus, QwQ-32B and Ollama
Hands-on tutorial on how to create a streamlined, powerful RAG pipeline that balances efficiency, accuracy, and scalability using the QwQ-32B model and Milvus.
