How to Make 4 Popular AI Applications with Milvus

 Cover image.
Cover image.
Milvus is an open-source vector database. It supports adding, deleting, updating, and near real-time search of massive vector datasets created by extracting feature vectors from unstructured data using AI models. With a comprehensive set of intuitive APIs, and support for multiple widely adopted index libraries (e.g., Faiss, NMSLIB, and Annoy), Milvus accelerates machine learning application development and machine learning operations (MLOps). With Milvus, you can rapidly develop a minimum viable product (MVP) while keeping costs at lower limits.
"What resources are available for developing an AI application with Milvus?” is commonly asked in the Milvus community. Zilliz, the company behind Milvus, developed a number of demos that leverage Milvus to conduct lightening-fast similarity search that powers intelligent applications. Source code of Milvus solutions can be found at zilliz-bootcamp. The following interactive scenarios demonstrate natural language processing (NLP), reverse image search, audio search, and computer vision.
Feel free to try out the solutions to gain some hands-on experience with specific scenarios! Share your own application scenarios via:
Natural language processing (chatbots)
Milvus can be used to build chatbots that use natural language processing to simulate a live operator, answer questions, route users to relevant information, and reduce labor costs. To demonstrate this application scenario, Zilliz built an AI-powered chatbot that understands semantic language by combining Milvus with BERT, a machine learning (ML) model developed for NLP pre-training.
👉Source code:zilliz-bootcamp/intelligent_question_answering_v2
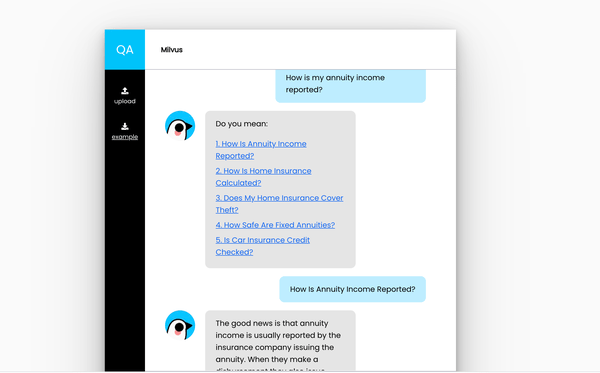 AI-powered chatbot built with Milvus and BERT.
AI-powered chatbot built with Milvus and BERT.
How to use
Upload a dataset that includes question-answer pairs. Format questions and answers in two separate columns.
After typing in your question, a list of similar questions will be retrieved from the uploaded dataset.
Reveal the answer by selecting the question most similar to your own.
👉Video:[Demo] QA System Powered by Milvus
How it works
Questions are converted into feature vectors using Google’s BERT model, then Milvus is used to manage and query the dataset.
Data processing:
- BERT is used to convert the uploaded question-answer pairs into 768-dimensional feature vectors. The vectors are then imported to Milvus and assigned individual IDs.
- Question, and corresponding answer, vector IDs are stored in PostgreSQL.
Searching for similar questions:
- BERT is used to extract feature vectors from a user's input question.
- Milvus retrieves vector IDs for questions that are most similar to the input question.
- The system looks up the corresponding answers in PostgreSQL.
Reverse image search systems
Reverse image search is transforming e-commerce through personalized product recommendations and similar product lookup tools that can boost sales. In this application scenario, Zilliz built a reverse image search system by combining Milvus with VGG, an ML model that can extract image features.
👉Source code:zilliz-bootcamp/image_search
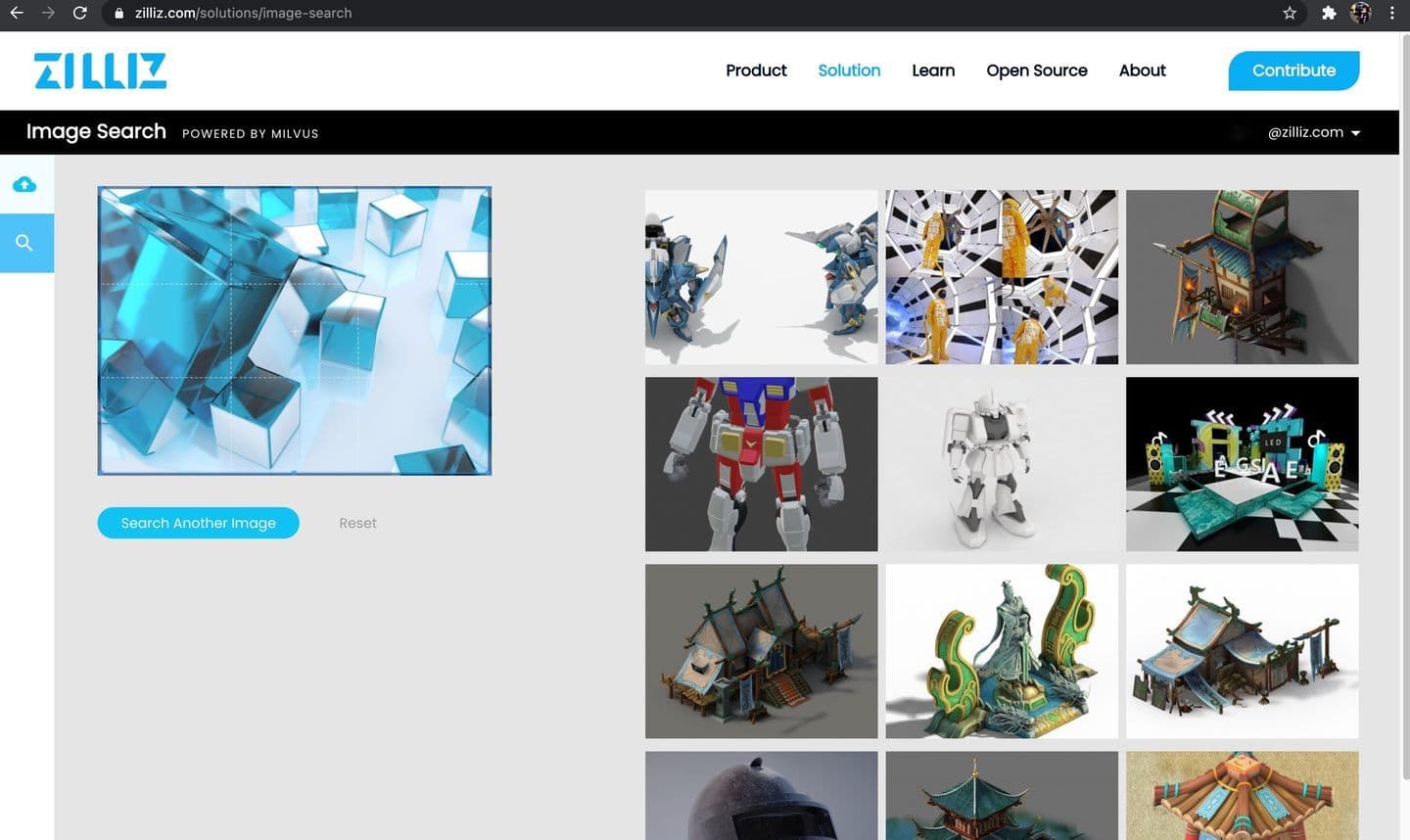 Reverse image search system built with Milvus and VGG.
Reverse image search system built with Milvus and VGG.
How to use
- Upload a zipped image dataset comprised of .jpg images only (other image file types are not accepted).
- Upload an image to use as the search input for finding similar images.
👉Video: [Demo] Image Search Powered by Milvus
How it works
Images are converted into 512-dimensional feature vectors using the VGG model, then Milvus is used to manage and query the dataset.
Data processing:
- The VGG model is used to convert the uploaded image dataset to feature vectors. The vectors are then imported to Milvus and assigned individual IDs.
- Image feature vectors, and corresponding image file paths, are stored in CacheDB.
Searching for similar images:
- VGG is used to convert a user’s uploaded image into feature vectors.
- Vector IDs of images most similar to the input image are retrieved from Milvus.
- The system looks up the corresponding image file paths in CacheDB.
Audio search systems
Speech, music, sound effects, and other types of audio search makes it possible to quickly query massive volumes of audio data and surface similar sounds. Applications include identifying similar sound effects, minimizing IP infringement, and more. To demonstrate this application scenario, Zilliz built a highly efficient audio similarity search system by combining Milvus with PANNs—a large-scale pretrained audio neural networks built for audio pattern recognition.
👉Source code:zilliz-bootcamp/audio_search
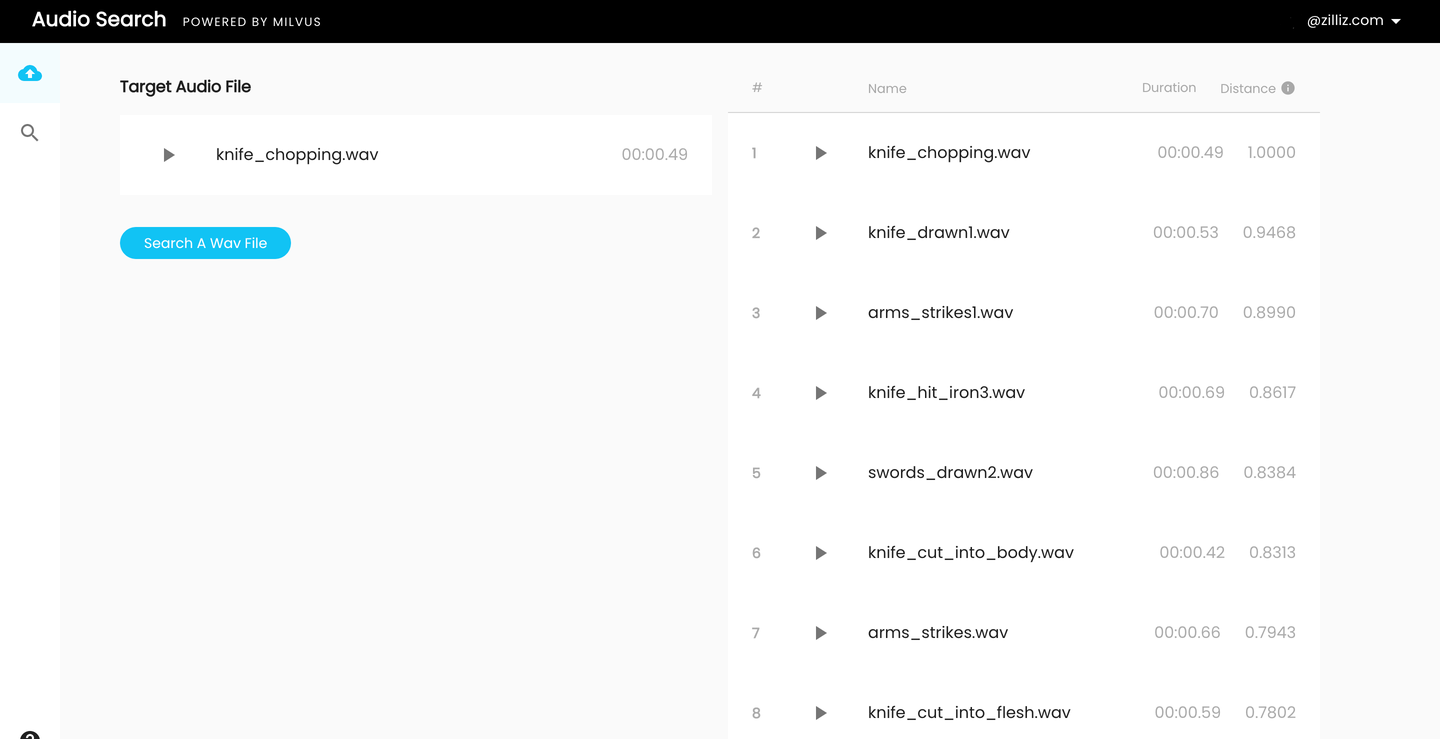 Audio search system built with Milvus and PANNs.
Audio search system built with Milvus and PANNs.
How to use
- Upload a zipped audio dataset comprised of .wav files only (other audio file types are not accepted).
- Upload a .wav file to use as the search input for finding similar audio.
👉Video: [Demo] Audio Search Powered by Milvus
How it works
Audio is converted into feature vectors using PANNs, large-scale pre-trained audio neural networks built for audio pattern recognition. Then Milvus is used to manage and query the dataset.
Data processing:
- PANNs converts audio from the uploaded dataset to feature vectors. The vectors are then imported to Milvus and assigned individual IDs.
- Audio feature vector IDs and their corresponding .wav file paths are stored in PostgreSQL.
Searching for similar audio:
- PANNs is used to convert a user’s uploaded audio file into feature vectors.
- Vector IDs of audio most similar to the uploaded file are retrieved from Milvus by calculating inner product (IP) distance.
- The system looks up the corresponding audio file paths in MySQL.
Video object detection (computer vision)
Video object detection has applications in computer vision, image retrieval, autonomous driving, and more. To demonstrate this application scenario, Zilliz built a video object detection system by combining Milvus with technologies and algorithms including OpenCV, YOLOv3, and ResNet50.
👉Source code: zilliz-bootcamp/video_analysis
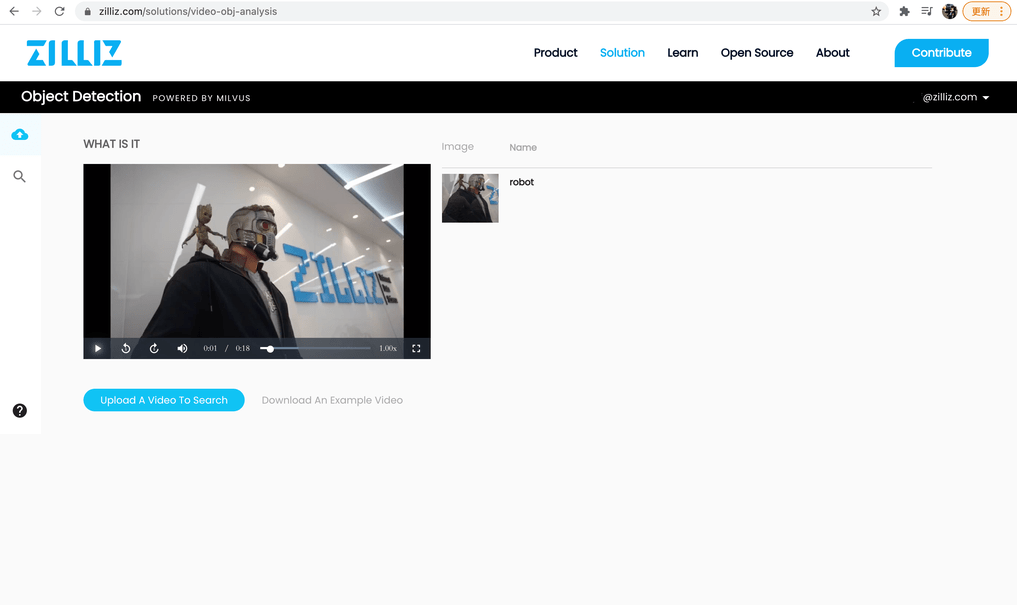 Video object detection system with Milvus.
Video object detection system with Milvus.
How to use
- Upload a zipped image dataset comprised of .jpg files only (other image file types are not accepted). Ensure that each image file is named by the object it depicts.
- Upload a video to use for analysis.
- Click the play button to view the uploaded video with object detection results shown in real time.
👉Video: [Demo] Video Object Detection System Powered by Milvus
How it works
Object images are converted into 2048-dimensional feature vectors using ResNet50. Then Milvus is used to manage and query the dataset.
Data processing:
- ResNet50 converts object images to 2048-dimensional feature vectors. The vectors are then imported to Milvus and assigned individual IDs.
- Audio feature vector IDs and their corresponding image file paths are stored in MySQL.
Detecting objects in video:
- OpenCV is used to trim the video.
- YOLOv3 is used to detect objects in the video.
- ResNet50 converts detected object images into 2048-dimensional feature vectors.
Milvus searches for the most similar object images in the uploaded dataset. Corresponding object names and image file paths are retrieved from MySQL.
Start Free, Scale Easily
Try the fully-managed vector database built for your GenAI applications.
Try Zilliz Cloud for FreeKeep Reading

The Real Bottlenecks in Autonomous Driving — And How AI Infrastructure Can Solve Them
Autonomous driving is data-bound. Vector databases unlock deep insights from massive AV data, slashing costs and accelerating edge-case discovery.
Zilliz Cloud Enterprise Vector Search Powers High-Performance AI on AWS
Zilliz Cloud delivers blazing-fast, secure vector search on AWS, optimized for AI workloads with AutoIndex, BYOC, and Cardinal engine performance.

DeepRAG: Thinking to Retrieval Step by Step for Large Language Models
In this article, we’ll explore how DeepRAG works, unpack its key components, and show how vector databases like Milvus and Zilliz Cloud can further enhance its retrieval capabilities.
