Beyond Chatbots: How Function Calling Makes AI Actually Useful
Beyond Chatbots: How Function Calling Makes AI Actually Useful
Introduction
Imagine having an AI assistant that doesn't just chat with you, but actually does things—checking the weather, booking appointments, controlling smart devices, or querying your database in real time. Function calling is the ability to reliably connect LLMs to external tools to enable effective tool usage and interaction with external APIs. This capability transforms static AI models into dynamic agents that can perform real-world actions, bridging the gap between natural language conversation and practical task execution.
What is Function Calling
Function calling lets you connect models to external tools and APIs. Instead of generating text responses, the model understands when to call specific functions and provides the necessary parameters to execute real-world actions. Think of it as giving your AI a toolkit—when you ask "What's the weather like in New York?", the model recognizes it needs weather data, identifies the appropriate weather API function, extracts the location parameter ("New York"), and formats a structured request that your application can execute.
Function Calling, often referred to as "Tool Use" in AI, allows AI models to interact with external tools or APIs to perform specific tasks. This feature extends the model's functionality beyond text generation by enabling it to execute actions, retrieve data, and interact with other systems dynamically.
The process doesn't involve the AI model directly executing code. Instead, you send descriptions of functions to the LLM, allowing it to format these as structured outputs in valid JSON format, which is aligned to a particular schema. Your application then uses these structured outputs to call the actual functions or APIs.
Key Features of Function Calling
Structured Output Generation: LLMs like GPT-4 and GPT-3.5 have been fine-tuned to detect when a function needs to be called and then output JSON containing arguments to call the function. This ensures reliable, parseable responses that your application can process consistently.
Schema Adherence: When you turn on Structured Outputs by setting strict: true in your function definition, Structured Outputs guarantees that the arguments generated by the model for a function call exactly match the JSON Schema you provided in the function definition.
Multi-Function Support: Models can work with multiple functions simultaneously. You can define more than one function in a single request, allowing for complex workflows that might require different tools or data sources.
Parallel Function Calling: Parallel function calling lets you execute multiple functions at once and is used when the functions are not dependent on each other. This capability enables efficient multi-tasking scenarios like gathering data from multiple independent sources.
Compositional Function Calling: Advanced models can chain multiple function calls together, creating sophisticated workflows where the output of one function becomes the input for another.
How Does Function Calling Work
Function calling follows a structured four-step process that ensures reliable interaction between your application, the AI model, and external tools.
Step 1: Define Function DeclarationsYou start by describing your functions using JSON Schema format. Function Declarations describe the function's name, parameters, and purpose to the model. Each function declaration includes the function name, a clear description of its purpose, parameter types, and which parameters are required.
Step 2: Send Request with Function DeclarationsSend user prompt along with the function declaration(s) to the model. It analyzes the request and determines if a function call would be helpful. If so, it responds with a structured JSON object. The model examines both the user's request and the available functions to decide whether external tools are needed.
Step 3: Execute the FunctionThe Model does not execute the function itself. It's your application's responsibility to process the response and check for Function Call and extract the function name and arguments. Your application then executes the corresponding function with the provided parameters.
Step 4: Return Results to ModelIf a function was executed, capture the result and send it back to the model in a subsequent turn of the conversation. It will use the result to generate a final, user-friendly response that incorporates the information from the function call.
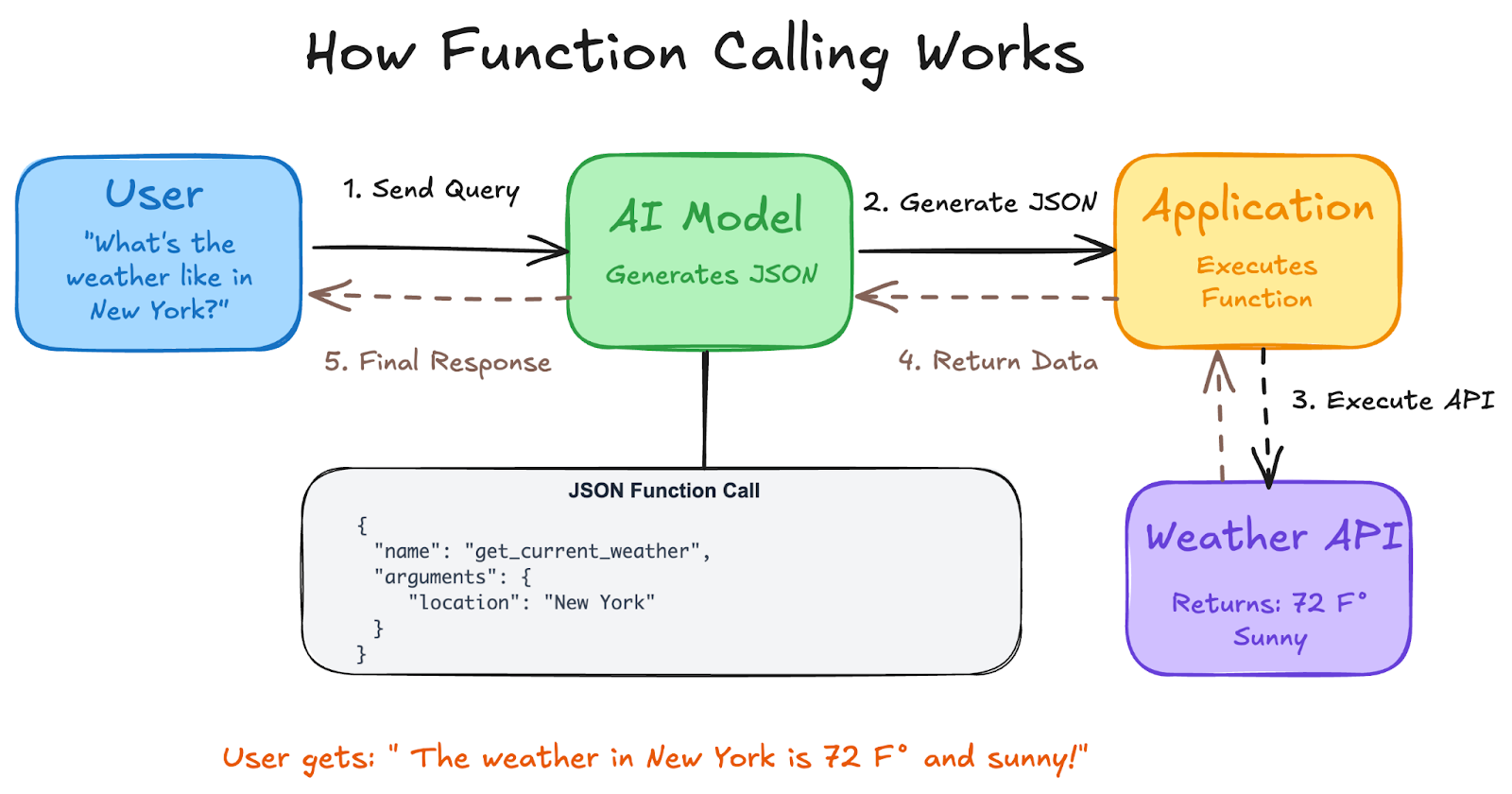 how function calling works.png
how function calling works.png
Benefits and Challenges of Function Calling
Benefits
Real-Time Accuracy: Function calling improves AI responses by accessing current, up-to-date information from external sources rather than relying on outdated training data.
Extended Capabilities: AI models can execute tasks outside their native abilities, such as accessing databases, performing calculations, or controlling IoT devices through external APIs.
Direct Task Execution: Models can interact directly with external systems to perform real-world actions like processing transactions, controlling devices, or retrieving specific data.
Code Reusability: Function schemas can be used across different models and applications, reducing development time and ensuring consistency.
Challenges
Security Risks: Untrusted data from external tools can instruct the model to perform unintended actions, requiring proper authentication, input validation, and user confirmation steps.
Error Handling Complexity: Network failures, API rate limits, and malformed responses can disrupt workflows, requiring robust error handling mechanisms and fallback strategies.
Performance Impact: Each function call adds latency to conversations, and managing multiple external API calls can impact user experience if not optimized properly.
Dependency Management: External APIs may change, become unavailable, or have different versioning requirements, creating ongoing maintenance challenges.
Comparison of Function Calling, Agent2Agent, and MCP
| Aspect | Function Calling | Agent2Agent (A2A) | Model Context Protocol (MCP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Connect AI models to external tools and APIs | Enable communication between multiple AI agents | Standardize how applications provide context to LLMs |
| Communication Type | Model-to-tool interaction | Agent-to-agent collaboration | Application-to-model context sharing |
| Scope | Single model calling external functions | Multi-agent coordination and collaboration | Unified interface for external data sources |
| Use Case Focus | Task execution (weather, payments, control) | Agents collaborating in natural language or mixed modalities | Agents calling structured functions, APIs, or tools |
| Development Level | Mature, widely implemented | Google released Agent2Agent (A2A) in April 2025 | Anthropic launched MCP in late 2024 |
| Relationship | Core capability | A2A focuses on the second category: coordination between intelligent agents | MCP focuses on the first category: organizing what agents, tools, or users send into the model |
| Standards | JSON Schema-based function definitions | Built on open standards: A2A uses HTTP, JSON-RPC, and SSE | Universal, open standard for connecting AI systems with data sources |
| Integration | Direct model feature | Complementary to function calling | Google carefully positioned A2A as a complementary protocol to MCP |
Use Cases of Function Calling
Customer Support Automation
An AI chatbot uses function calling to perform actions such as resetting passwords, scheduling appointments, or updating customer records by directly interacting with a company's internal systems or databases. This enables support agents to resolve issues faster and provide 24/7 assistance.
E-commerce Integration
An AI-driven shopping assistant can process payments or check product availability in real-time by calling the relevant APIs. Customers can ask natural language questions like "Do you have this in size medium?" and get real-time inventory responses.
Smart Home Control
Voice-activated assistants use function calling to control smart devices like lights, thermostats, and security systems. Users can say "Set the living room to romantic lighting," and the system translates this to specific device commands.
Data Extraction and Processing
LLM-powered solutions for extracting and tagging data (e.g., extracting people's names from a Wikipedia article) enable automated content processing and information management workflows.
Financial Services
Function calling enables AI assistants to check account balances, transfer funds, pay bills, or analyze spending patterns by securely connecting to banking APIs with proper authentication and user consent.
Development Tools
Applications that can help convert natural language to API calls or valid database queries streamline development workflows and reduce the technical barrier for database interactions.
FAQs on Function Calling
What's the difference between function calling and the AI actually running code?
Function calling as a term is often misunderstood: many believe the model is actually executing the function call, when in fact it's only providing the parameters. The AI generates structured instructions, but your application executes the actual functions.
Can function calling work with any external API?
Yes, as long as you can define the API's interface using JSON Schema format and handle the API calls in your application code. Function calling with APIs involves the AI model identifying when a task requires external data, selecting the appropriate API, sending the required parameters, and then integrating the returned information into its response.
Is function calling secure for sensitive operations?
Function calling can be secure when properly implemented with authentication, input validation, and user confirmation steps. Implement User Confirmation Steps: Particularly for functions that take actions, we recommend including a step where the user confirms the action before it's executed.
What happens if a function call fails?
Your application should implement robust error handling to manage API failures, network issues, or invalid responses. The AI can then provide helpful error messages or suggest alternative approaches based on the error information you provide.
Can multiple functions be called at once?
The model also supports calling multiple functions in a single turn (parallel function calling) and in sequence (compositional function calling). This enables complex workflows and efficient task execution.
Do all AI models support function calling?
Most modern large language models from major providers support function calling, but implementation details and capabilities may vary. Check your specific model's documentation for supported features and limitations.
- Introduction
- What is Function Calling
- Key Features of Function Calling
- How Does Function Calling Work
- Benefits and Challenges of Function Calling
- Comparison of Function Calling, Agent2Agent, and MCP
- Use Cases of Function Calling
- FAQs on Function Calling
Content
Start Free, Scale Easily
Try the fully-managed vector database built for your GenAI applications.
Try Zilliz Cloud for Free